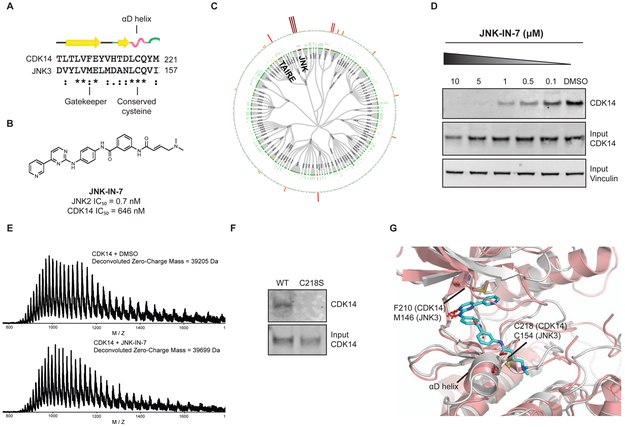
Figure 1:
CDK14 is a covalent target of JNK-IN-7. (A) Sequence alignment of α-D loop of JNK3 and CDK14. (B) Chemical structure and biochemical potency of JNK-IN-7. (C) Kinativ profiling of JNK-IN-7 cellular selectivity at 1 μM. (D) Biotinylated JNK-IN-7 can pull down CDK14 from treated cell lysates. JNK-IN-7 shows dose dependent competition with biotin-JNK-IN-7. (E) Intact mass spectrum of recombinant CDK14 protein incubated with JNK-IN-7, resulting in mass shift compared to DMSO. (F) Biotin-JNK-IN-7 can pull down WT CDK14-flag, but not C218S CDK14-flag from HEK293 lysates, demonstrating that covalent bond formation occurs with the native protein. (G) Overlay of the crystal structure of JNK3 with the homology model of CDK14, showing spatial proximity of targeted cysteine residues. See also Figure S2.