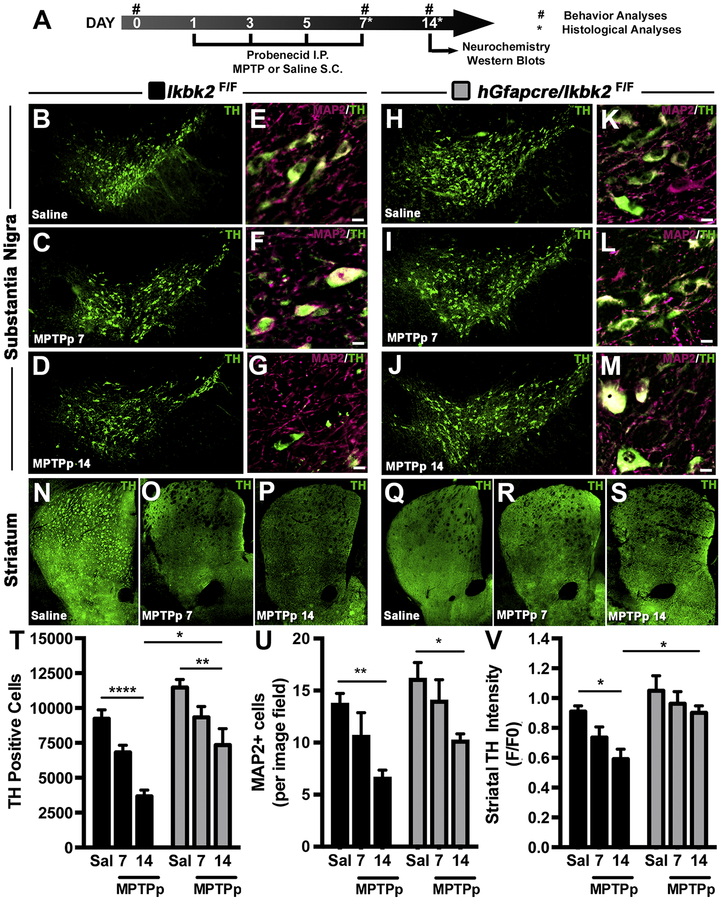
Figure 3.
MPTP-induced loss of dopaminergic neurons and neuronal projections is decreased in hGfapcre/Ikbk2F/F mice. A. Schematic of treatment and experimental regimen for the study. B-M. The number of TH+ neurons (green) in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) was assessed via immunofluorescence-based stereology and presented as representative montages for Ikbk2F/F (B-D) and hGFAP-Cre/IkkβF/F mice (H-J). Total neuronal loss was determined via counts of MAP2+ neurons within the SNpc through immunofluorescence and presented as representative images showing MAP2 (magenta) and TH (green) for Ikbk2F/F (E-G) and hGFAP-Cre/IkkβF/F mice (K-M). N-S. Loss of dopaminergic nerve terminals was assessed via quantification of immunofluorescence intensity of TH in the striatum (ST) as shown in representative montages for Ikbk2F/F (N-P) and hGFAP-Cre/IkkβF/F mice (Q-S). T. Quantitative stereological counts estimating the total number of TH+ neurons presented as an average number of TH+ cells ± SEM. U. Quantitative counts of MAP2+ neurons to estimate total neuronal loss presented as an average number of MAP2+ cells per image field ± SEM. V. Loss of striatal TH intensity was quantified via measuring total striatal TH intensity and normalized to saline Ikbk2F/F mice. Data is presented as average TH intensity ± SEM. Data was analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer post hoc test (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and **** p < 0.0001).