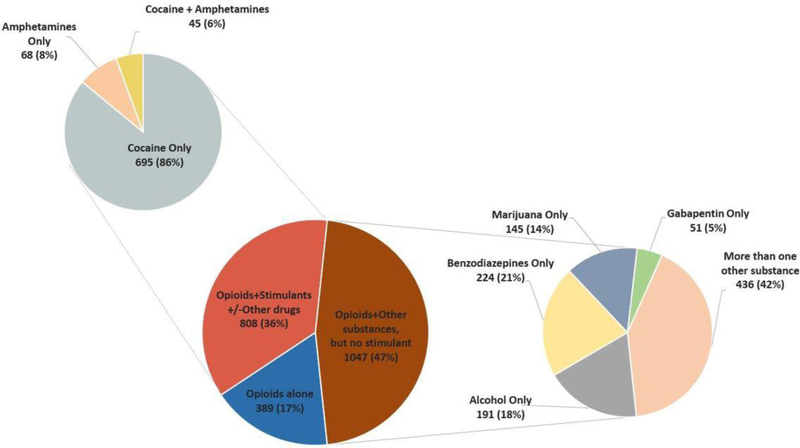
Figure 1. Opioid-related overdose deaths with accompanying toxicology, 2014 and 2015, combined (n=2,244).
This figure demonstrates the proportion of opioid-related overdose deaths by accompanying substances found on toxicology. Deaths were divided into three mutually exclusive groups: (1) opioid-related deaths with opioids only present on toxicology (dark blue), (2) opioid-related deaths with opioids and stimulants (with or without other substances) present on toxicology (red), and (3) opioid-related deaths with opioids and other substances not including stimulants present on toxicology (green). Opioids include any of the following: opiates, fentanyl and fentanyl analogs, tramadol, heroin, hydrocodone, morphine, oxycodone, codeine, hydromorphone, oxymorphone, or prescription opioids not otherwise classified). Stimulants include either cocaine or amphetamines. “Other substances” include any of the following: benzodiazepines, alcohol, marijuana, gabapentin, or clonidine. Smaller pie charts distinguish the specific stimulant or other substance present on toxicology.