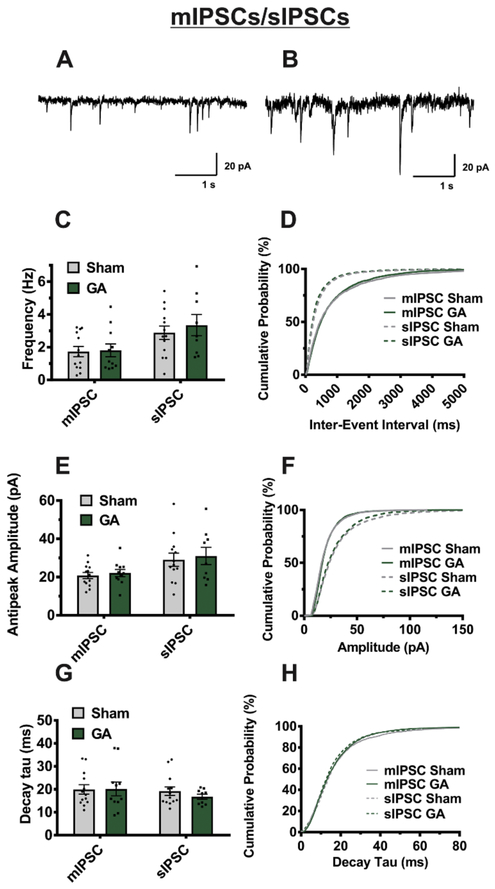
Figure 6. Miniature and spontaneous IPSCs are unaffected by neonatal GA exposure.
A,B Representative traces from an mIPSC and sIPSC, respectively, recorded from two different VB neurons (sham animal). Averages from multiple VB cells show no significant difference between sham and GA treated animals in event frequency for both mIPSCs (sham n=13 cells from 6 animals, GA n=11 cells from 5 animals; t(22)=.152, p=.880) and sIPSCs (sham n=13 cells from 7 animals, GA n=9 cells from 5 animals; t(20)=.639, p=.53). E GA exposure likewise has no significant effect on amplitude of mIPSCs (t(22)=.541, p=.594) or sIPSCs (t(20)=.348, p=.731) G Decay tau is also unaffected by GA exposure in mIPSCs (t(22)= .063, p=.950) and sIPSCs (t(20)=.987, p=.336) D, F, and H are respective cumulative probability plots of said parameters illustrating the lack of change in mIPSCs (sham n= 1733 events, GA n=1186 events) and sIPSCs (sham n=915 events, GA n=1204 events).