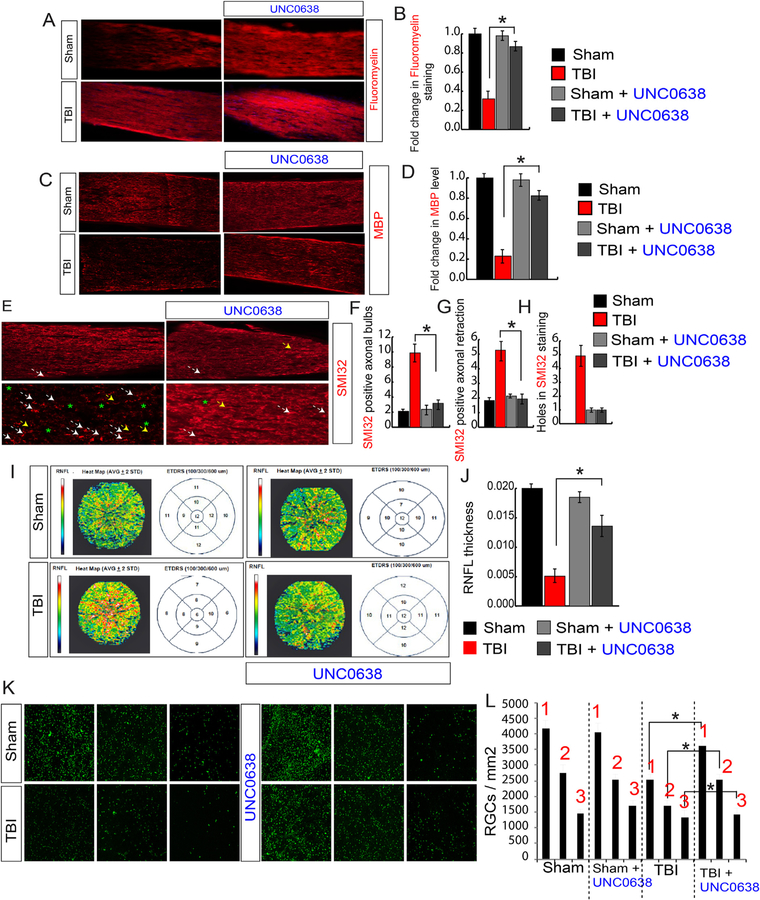
Fig. 7. Treatment with UNC0638 rescues demyelination, abnormalities in neurofilaments, and RNFL thickness following TBI.
(A, B) Confocal microscopic analysis (A) and the quantitative analysis (B) show that a loss of Fluoromyelin red staining after TBI was rescued in TBI + UNC0638 treated mice. (C–D) Confocal microscopic analysis (C) and the quantitative analysis (D) show that a loss of MBP staining after TBI was rescued in TBI + UNC0638 treated mice. (E–H) The confocal microscopy (E) and the quantitative analysis (F–H) show that an increase in SMI-32 positive axonal bulbs (F), the axonal retraction (G) and holes (H) was recovered in optic nerve isolated from TBI + UNC0638 mice. (I–J) The SD-OCT data shows that the RNFL thickness has been decreased in ETDRS measured after 100, 300 and 600 μM diameter in TBI; however, it was rescued in TBI-mice treated with UNC0638 (I). The quantitative analysis of RNFL thickness measured by SD-OCT in both TBI and sham mice treated with or without UNC0638 (J). (K–L) The Fluorogold (FG) staining suggests that TBI-induced loss of RGCs was rescued in TBI-mice treated with UNC0638. Box 1, 2 and 3 are 0.5 mm, 1 mm and 1.5 mm from the center. Statistical significance was measured by one-way ANOVA with a Tukey-Kramer post-hoc correction, n = 5, *p < 0.05. All data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)