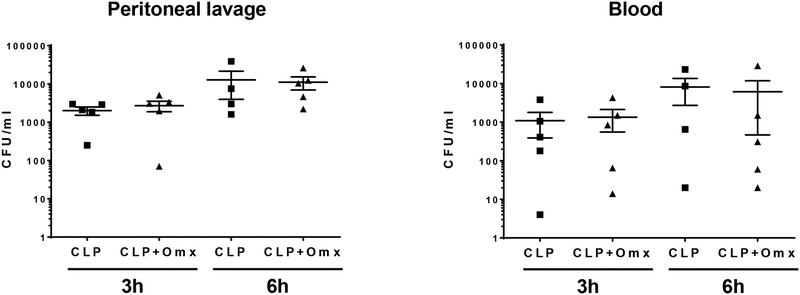
Fig. 4.
Removal of the omentum did not change bacterial loads within the peritoneal cavity or blood after CLP. Male CD-1 mice were subjected to CLP (16-gauge needle perforation) or omentectomy+CLP (16-gauge needle perforation), and peritoneal lavage and blood were collected at 3 h or 6 h post CLP. Peritoneal lavage and blood samples (n=?) were serially diluted in PBS spread on Trypticase Soy Agar plates containing 5% Sheep Blood. All plates were incubated for 24 h at 37°C. The number of bacterial colonies was counted and expressed as CFU per milliliter of blood or peritoneal lavage fluid. Statistical analysis for the comparison between groups was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test.