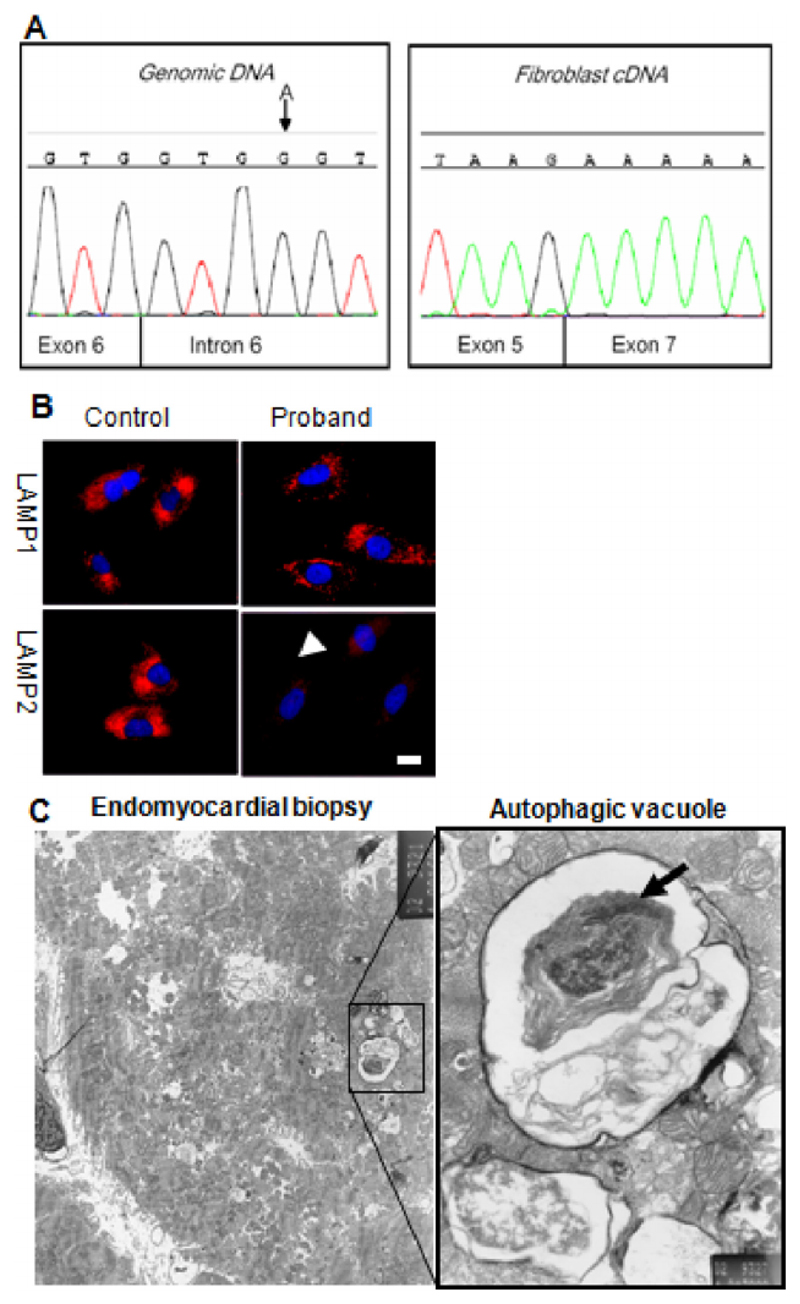
Fig. 2.
Investigations for confirming diagnosis of Danon disease. A: Genomic DNA sequencing of LAMP2 showed an A G mutation in the intron 6 splice site (left panel) a described mutation known to cause skipping of exon 6. This is confirmed in cDNA sequencing from fibroblasts (right panel) which reveals an in frame fusion of exons 5 and 7. B: Skin fibroblasts cultured from the proband were stained for the glycosylated lysosomal membrane proteins LAMP1, and LAMP2 (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue). Cells from the proband show markedly reduced staining of immunoreactive LAMP2 polypeptide localizing to brightly staining LAMP1 positive intracellular particles (lysosomes). This is compatible with a mutation resulting in reduced abundance of the full-length protein product; this was confirmed by Western blot analysis (data not shown). Scale bar: 10 μm. C: Septal endomyocardial biopsies were taken from the right ventricle of the proband and prepared for electron microscopy. Several fibres feature autophagic vacuoles and are shown in the expanded pane to contain mitochondria (arrow), and electron-dense debris representing partially degraded cytoplasmic contents. Scale bar: 1 μm.