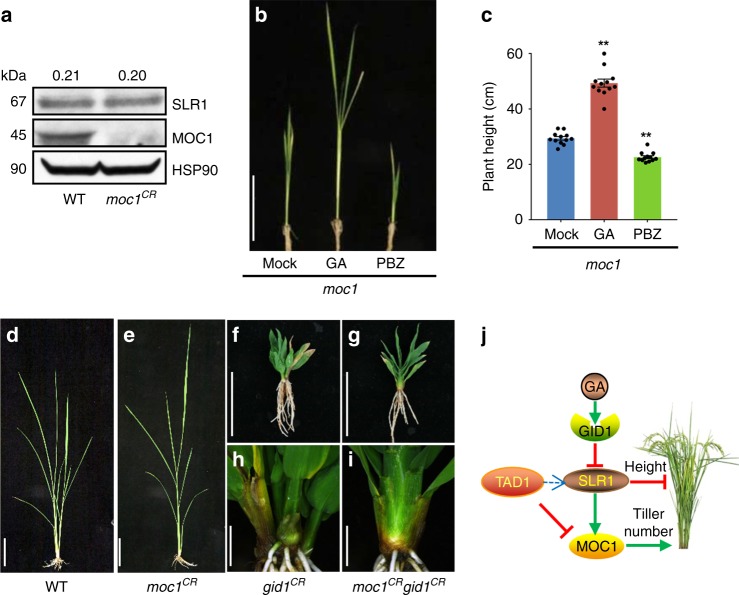
Fig. 5.
Controls of plant height by GA independently of MOC1. a Protein levels of SLR1 and MOC1 in the WT and moc1CR, determined by protein blotting using α-SLR1 and α-MOC1. HSP90, loading control. Values above panels indicate signal strength for SLR1 in arbitrary units determined by densitometry. The full scans of immunoblots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 12. b Effects of GA and PBZ treatments on plant height of moc1. Scale bar, 20 cm. c Quantitation of the plant height shown in (b). Asterisks indicate significant difference to the mock (two-tailed Student’s t test, **p < 0.01; mean ± s.e.m., n = 12). d–i Phenotypes of the WT, moc1CR, gid1CR, and moc1CR gid1CR after 2 months of growth. h, i show the magnified shoot bases of (f) and (g), respectively. d, e Scale bar, 20 cm; (f, g), scale bar, 5 cm; (h, i), scale bar, 0.5 cm. j A model of GA signaling and MOC1 regulation of plant height and tiller number in rice. Source data are provided as a Source Data file