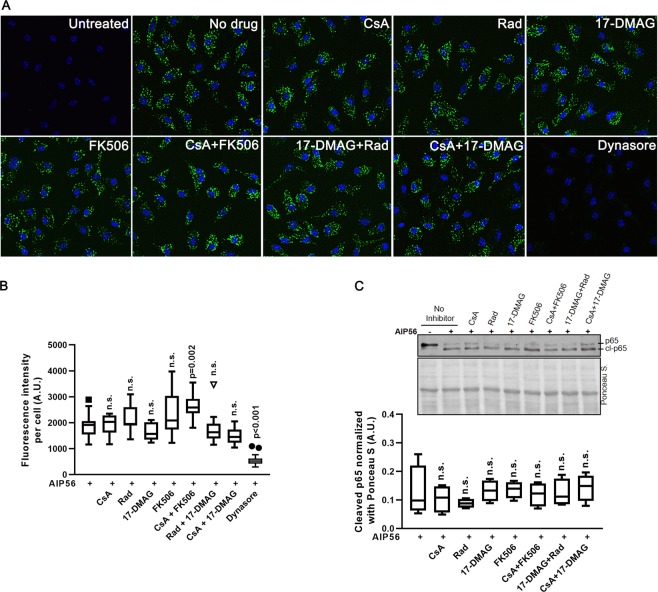
Figure 2.
Pharmacological inhibition of Hsp90 and cyclophilins has no effect on the endocytic uptake and catalytic activity of AIP56. (A) mBMDM were left untreated or treated with the indicated inhibitors (10 µM Rad and 20 µM 17-DMAG, CspA or FK506), alone or at the indicated combinations, before incubation with 170 nM AIP56-488 for 30 min on ice followed by 15 min at 37 °C. As control, cells were incubated with 80 µM of the dynamin inhibitor dynasore, previously shown to inhibit AIP56 endocytosis. The cells were fixed and nuclei were stained with DAPI. Images were acquired using IN Cell Analyzer 2000 (GE Healthcare) with a 20 × objective. Images shown are representative microscopic fields from one experiment. (B) Box-plot showing the quantification of the fluorescence intensity per cell (n = 3 independent experiments). In each experiment, a minimum of 500 cells per condition were analysed. Statistical significance was tested by one-way ANOVA and p-values for individual comparisons to cells treated only with toxin were calculated using the Dunnett’s test. (C) The metalloprotease activity of AIP56 is not affected by the inhibitors used in this study. Sea bass peritoneal cell lysates (containing sea bass p65) were incubated for 3 h at 22 °C with 100 nM recombinant AIP56 in the presence of Rad, CsA, 17-DMAG or FK506, alone or combined, and cleavage of p65 assessed by western blotting (chromogenic detection). Lysates incubated with the toxin in the absence of the inhibitors were used as controls. A representative blot is shown (the full-length blot is presented in Fig. S7). The box-plot shows the quantification of the cleaved p65 (n = 4 independent experiments). Loading correction was achieved by dividing the density of the cleaved p65 by the respective density of Ponceau S. Statistical significance was tested by one-way ANOVA and p-values for individual comparisons to cell lysates treated only with toxin were calculated using the Dunnett’s test.