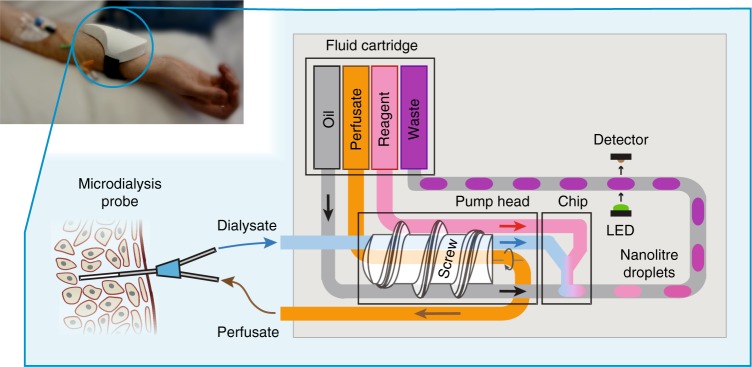
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram illustrating the operation of the device. The screw-driven peristaltic pump simultaneously feeds perfusate into a microdialysis probe and withdraws the resulting dialysate into the device. From the pump, dialysate is delivered into a microfluidic chip, where an analyte-specific reagent is added, and the resultant flow immediately segmented into a stream of droplets by the addition of an immiscible oil. Within the droplets, the reagent reacts with the analyte to produce a measurable optical response. The droplets flow out of the chip into low-volume PTFE tubing and downstream to an optical flow cell where the product of the reaction is quantified31. A microcontroller (not shown) saves the result to a micro SD card and relays it via Bluetooth to an external device. The analysed droplets are collected in a waste sachet for later disposal. An image illustrating a sensor being used in a clinical setting to monitor tissue is shown top-left