Fig. 2.
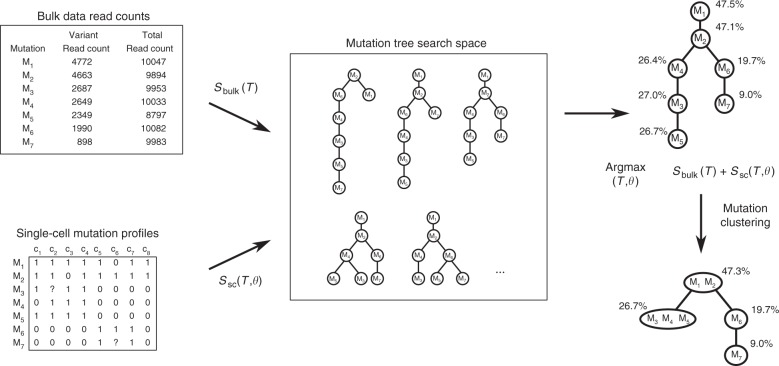
B-SCITE uses a Markov chain Monte Carlo approach to search the space of candidate mutation histories. Each candidate tree is scored based on its joint fit to the single-cell and bulk DNA sequencing data. The bulk data consist of a high-coverage variant and total read counts for the mutated loci. The single-cell data consist of the observed mutation profiles of the sequenced cells. These single-cell profiles are characterised by high noise rates (θ) that are learned from the SCS data along with the tree topology T. B-SCITE reports the tree with the highest joint score. This tree is a fully resolved mutation tree. To obtain a clonal tree, the linear tree parts can be clustered based on the variant allele frequencies of the bulk data