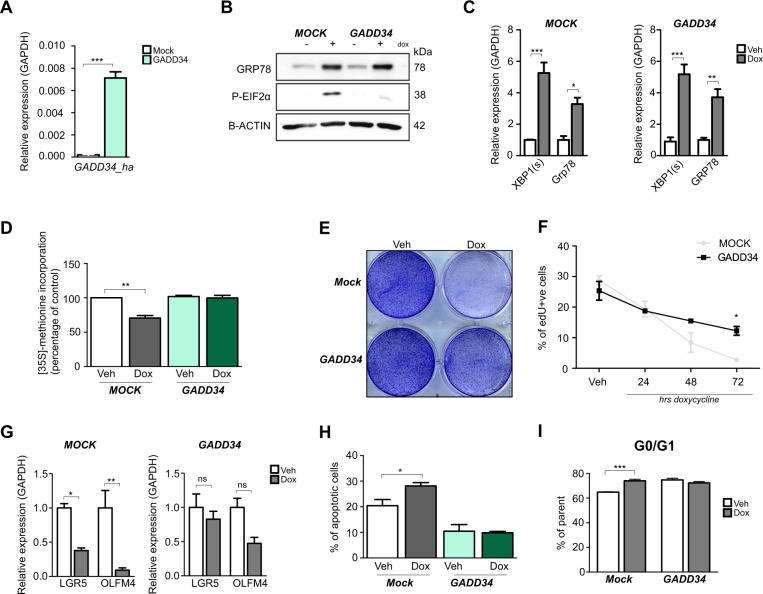
Fig. 4. Inhibition of eIF2α phosphorylation rescues XBP1(s) induced growth arrest.
a Quantitative RT-PCR analysis for hamster GADD34 in cells expressing either a mock or a GADD34 vector. b Protein levels of GRP78 and phosphorylated eIF2α in LS174T XBP1(s)Tet On cells expressing either a mock or a GADD34 vector. c Quantitative RT-PCR analysis for XBP1(s) and downstream target genes upon induction of XBP1(s) expression in the presence of either a mock or a GADD34 vector. d Global protein translation rate, measured by 35SMethionine incorporation assay. e Crystal violet cell viability assay in LS174T XBP1(s)Tet On cells. f FACS-based EdU incorporation assay in LS174T XBP1(s)Tet On cells; assay was performed after 2 h of EdU incorporation. g Quantitative RT-PCR analysis for intestinal stem cell markers LGR5 and OLFM4. h Percentage of apoptotic cells, measured with propidium iodide and Annexin V staining on Flow Cytometry. (i) Quantification of cell cycle analysis performed on Flow Cytometry using propidium iodide. All data are shown as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001