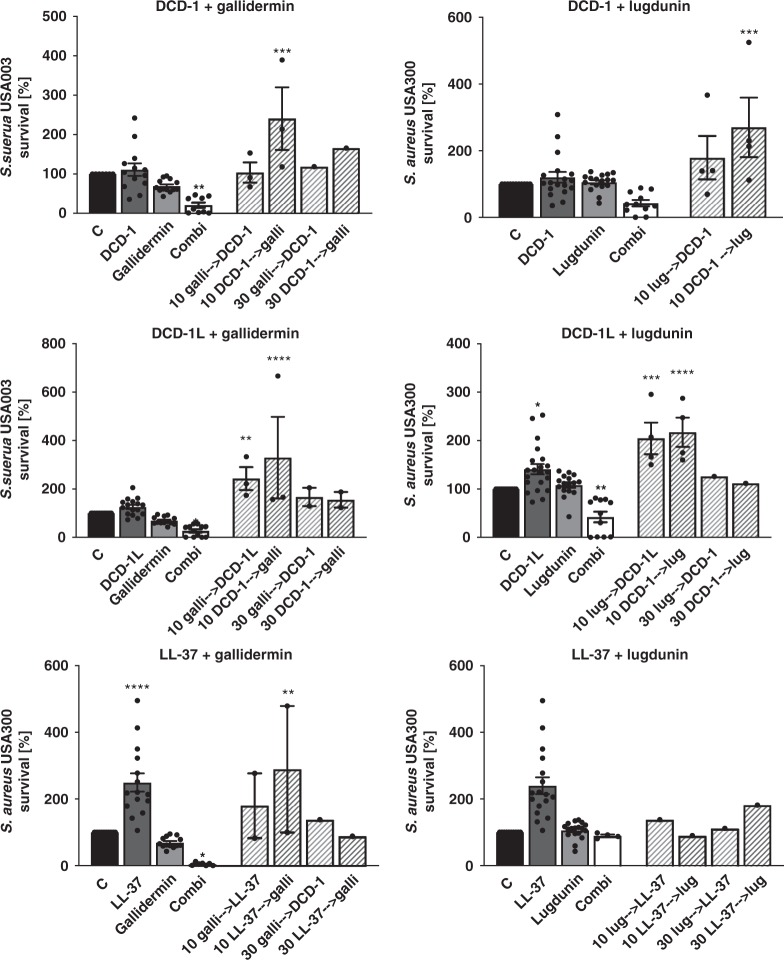
Fig. 6.
Simultaneous treatment of peptides exhibits antimicrobial activity. Logarithmically grown (3 × 106) S. aureus were simultaneously (filled bars; combination treatment (Combi), white bars) or sequentially (striped bars) incubated with 2 µM of human antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) (dark gray bars), 2 µM lugdunin, and 0.8 µM gallidermin (both light gray bars) diluted in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 0.1% tryptic soy broth (TSB) in a 96-well V-plate. After 10 or 30 min incubation with the first single peptide at 37 °C and orbital shaking, bacteria were collected via centrifugation and were resuspended in a dilution containing the second peptide for 2 h and 50 min, or 2 h and 30 min, respectively. Several dilutions of the bacterial suspensions were plated onto TSB agar plates and incubated overnight at 37 °C. The next day S. aureus CFUs were counted. Each experiment was performed in triplicates. Data represent the percentage of CFU normalized to the untreated control ± s.e.m. Significant differences to control treatments were analyzed by ordinary one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001). Source data are provided as a Source Data file