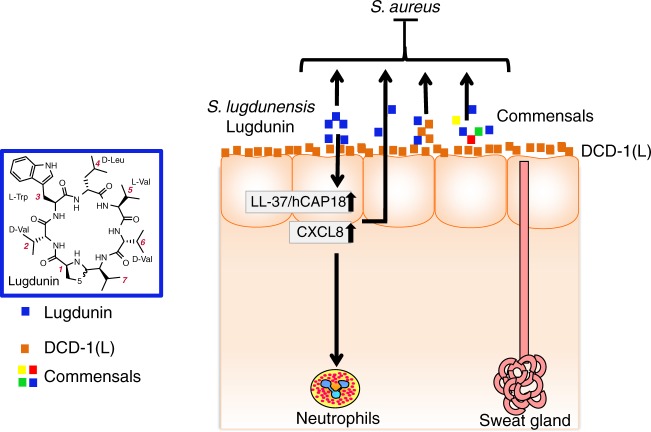
Fig. 7.
Proposed model of lugdunin-mediated skin protection. Lugdunin acts on different levels to protect against S. aureus skin infection: First it can directly inhibit and kill S. aureus. Secondly, it can cooperate with host-derived antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) such as hCAP18/LL-37 and the dermcidin-derived peptides DCD-1(L) to kill S. aureus. Additionally, on a third level of protection, lugdunin induces an innate immune response of the skin, which leads to the recruitment of phagocytic immune cells, which will clear potentially invading pathogens. Finally, this innate immune response can be highly amplified by factors derived from the skin commensal S. epidermidis. Blue, lugdunin; orange, DCD-1(L); multicolored, commensals