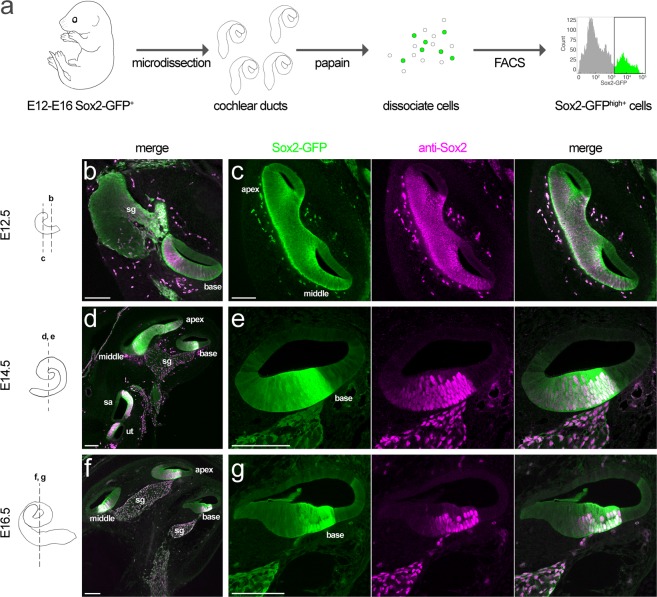
Figure 1.
Sox2-EGFP expression in prosensory cells of the embryonic cochlea. (a) Shows the tissue isolation and FACS pipeline used to generate the cells. (b–f) Show Sox2-EGFP expression (green) in vibratome sections of cochlea at the indicated stages of embryonic development. Sox2 immunofluorescence (magenta) demonstrates both the prosensory cells in the cochlear duct and the glia of the spiral ganglion. Note that Sox2-EGFP expression corresponds to Sox2 immunofluorescence and that Sox2-EGFP developmental dynamics mirror those of endogenous Sox2 expression. For example, the Sox2+/Sox2-EGFP+ field of cells in the floor of the cochlear duct narrows between E12.5-16.5—first at the base of the duct, then apically (compare b,d and f) and first at the lateral side of the duct, then medially (compare c, e and g). The localization of Sox2-EGFP expression shown here is representative of that in at least three temporal bones. Scale bars = 100 μm. sg, spiral ganglion; sa, saccule; ut, utricle.