Figure 3.
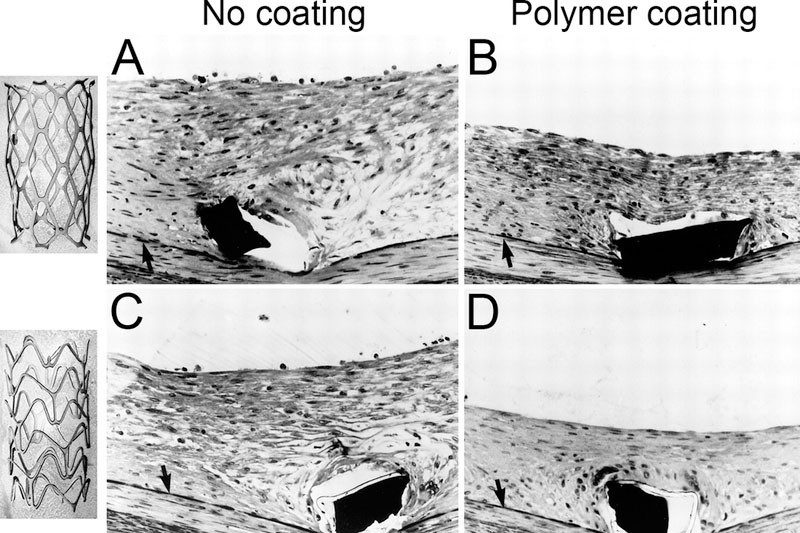
Stent surface and geometry significantly affect vascular injury and neointimal hyperplasia.5 Two bare metal stent (BMS) where fabricated using the same metal, process, and net surface area, on in a slotted tube (upper left panel) and the other corrugated ring (lower left panel) configuration and implanted in rabbit femoral arteries. Histologic examination was performed on methylmethacyrlate-embedded specimens harvested two weeks following placement. A, B uncoated surface; C, D polymer coated surface. Internal elastic lamina (arrow), stent struts (black rectangles), and polymer material (white rim circumscribing stent strut in C & D). Adapted from Edelman and Rogers.5
