Figure 4.
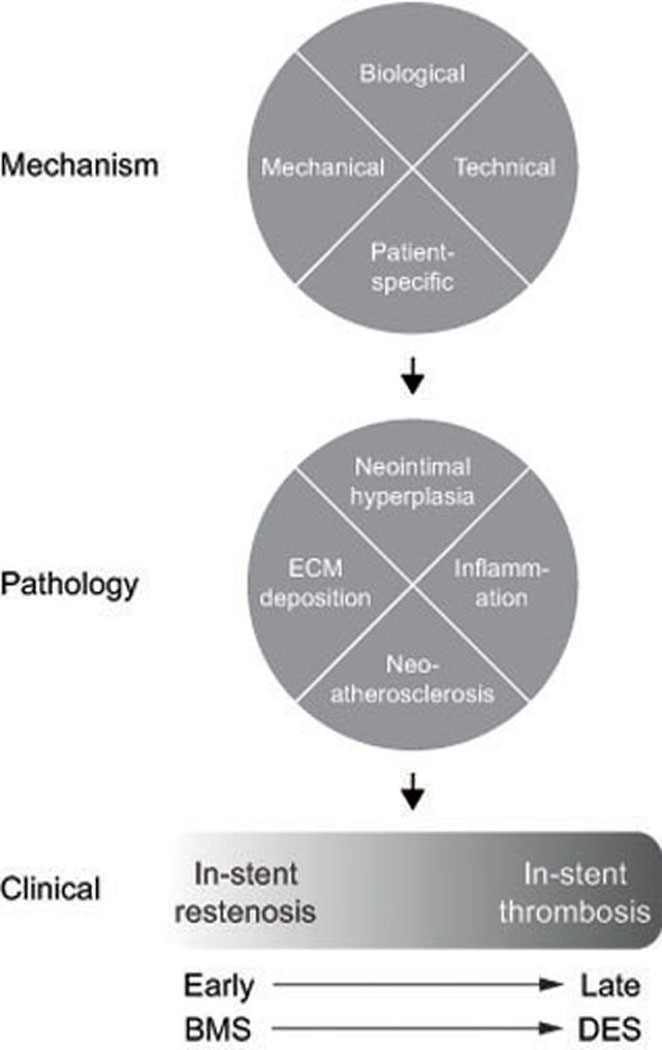
Schematic of the mechanisms and pathology mediating clinical in-stent restenosis and thrombosis, which likely lies on a shared continuum that shifts from early events associated with bare metal stents (BMS) to late events, associated with drug eluting stents (DES). Biological factors include vascular injury, malapposition with fibrin deposition, and non-uniform drug delivery; mechanical factors include stent under-expansion, hemodynamic stress, and stent fracture; technical factors include balloon barotrauma, stent gap and overlap, and residual untreated plaque; and patient-specific factors such as comorbidities, drug resistance, and hypersensitivity. Extracellular matrix = ECM.
