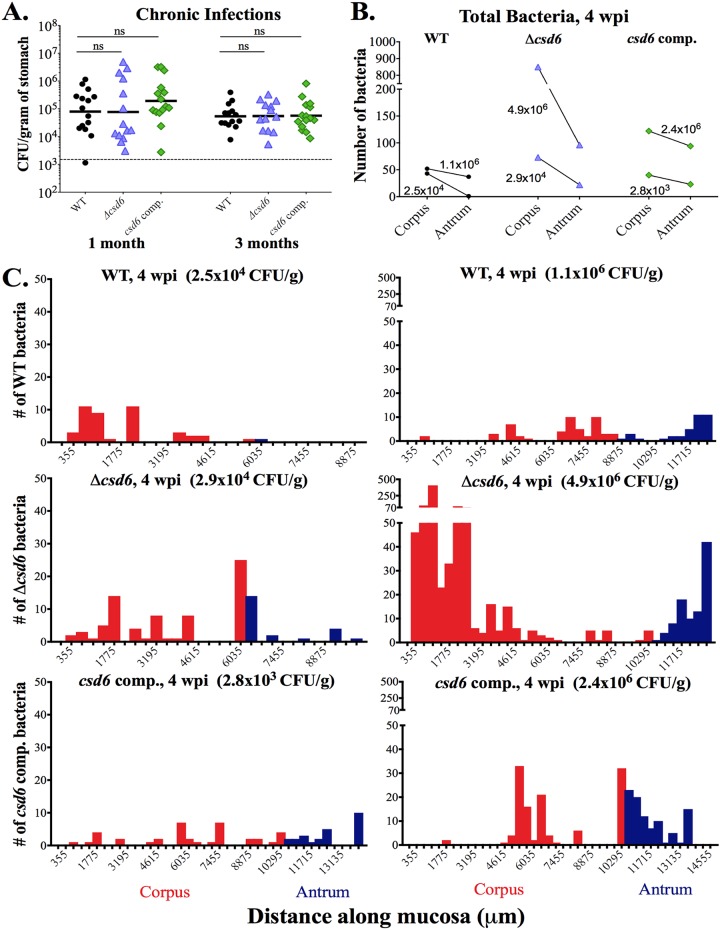
FIG 4.
Both wild-type H. pylori and the Δcsd6 straight-rod mutant can expand into the corpus by 1 month postinfection. Single infections were performed with the wild-type strain, Δcsd6 mutant, csd6 complemented strain, or broth (mock infection control). (A) Stomach loads at 1 month and 3 months postinfection. ns, not significant by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple-test correction. Data are from two independent experiments with n = 15 mice per group; the limit of detection is shown with a dotted line. (B and C) Thick stomach sections from the 1-month infections shown in panel A were stained for H. pylori, and the number of bacteria within the glands was quantified along the entire length of the section. For each bacterial strain, a mouse with a low CFU load (left) and a high CFU load (right) was analyzed. (B) The total number of bacteria in the corpus and antrum is shown for n = 2 mice per bacterial strain and is from one experiment, with the CFU per gram of stomach for each mouse indicated on the graph. (C) Gland analysis for wild-type H. pylori, Δcsd6 mutant, and csd6 complemented strains, showing the number of bacteria within corpus and antral glands along the length of the stomach in microns. Two mice were analyzed per group from one experiment. Red bars indicate the corpus and blue indicates the antrum. WT, wild type; comp, complemented; wpi, week postinfection.