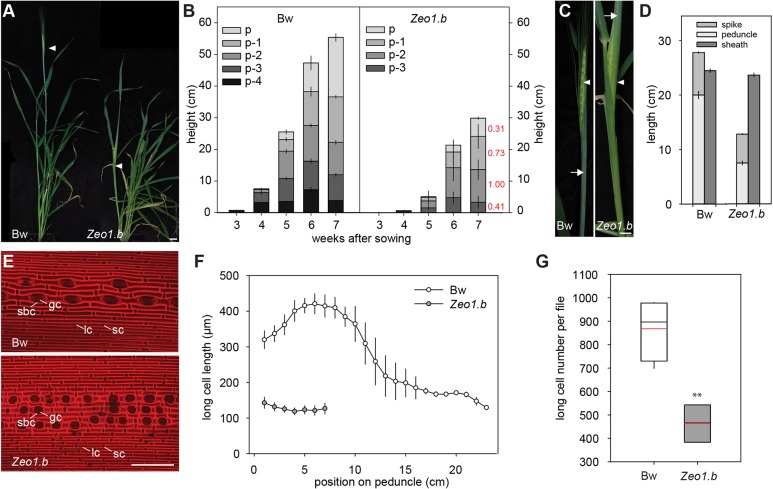
Fig. 1.
Internode growth and anatomy. (A) Glasshouse-grown Bowman (left) and Zeo1.b (right) plants at heading. Arrowheads indicate the spike. (B) Internode elongation in Bowman and Zeo1.b. Internode labels show position relative to peduncle (p) (n=16/genotype). Numbers in red show proportion of each Zeo1.b internode's length compared with Bowman at 7 weeks. (C) Emerged Bowman spike (left) and enclosed Zeo1.b spike (right). Arrowheads point to spike, arrows to flag leaf sheath. (D) Bowman and Zeo1.b peduncle, flag leaf sheath and spike lengths (n=17 Bowman; n=15 Zeo1.b). (E) Propidium iodide-stained epidermis from Bowman (top) and Zeo1.b (bottom) peduncles. (F) Average long-cell length (µm) per 1 cm peduncle segment (n=3/genotype). (G) Estimated number of long cells per file in Bowman and Zeo1.b peduncles. Box plots show 25th to 75th percentiles; whiskers extend down to 10th and up to 90th percentiles; black line shows median; and red line shows mean. Bw, Bowman; gc, guard cell; lc, long cell; sbc, subsidiary cell; sc, silica-cork cell pair. **P=0.004 (Student's t-test). Scale bars: 2 cm (A); 1 cm (C); 100 μm (E). Error bars represent s.e.m.