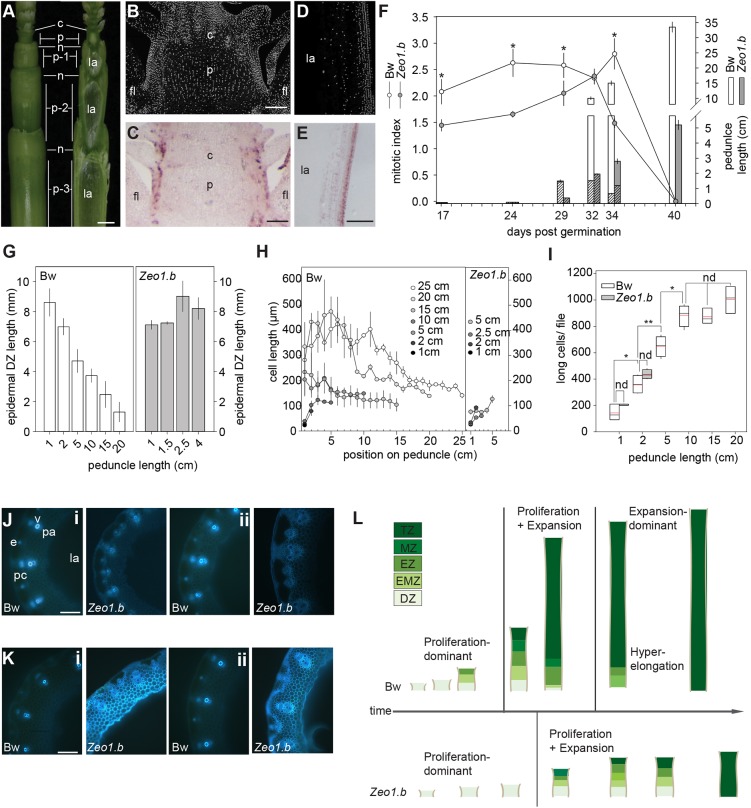
Fig. 2.
Developmental origin of Zeo1.b semi-dwarfism. (A) Intact upper barley stem (left) and after sectioning down the middle plane with a razor blade (right). Internodes numbered with respect to the peduncle internode. Leaves removed for clarity. (B-E) DAPI-stained sections (B,D) and in situ hybridisation with antisense HISTONE H4 (H4) probe (C,E) through Bowman peduncle initials at 24 days dpg (B,C), and through elongating 1.5 cm Bowman peduncles at 29 dpg (D,E). (F) Lines show average mitotic index of peduncle division zones and bars indicate peduncle length with hatched segments denoting the division zone region (n=3/genotype). (G) Proximo-distal length of the epidermal division zones in Bowman and Zeo1.b peduncles (n=3/genotype). (H) Long cell length (µm) per 1 cm segment of Bowman and Zeo1.b growing peduncles at defined lengths (n=10 cells/segment/3 biological replicates/genotype). (I) Peduncle cell number per file at defined peduncle lengths during growth (n=3/genotype/length). (J,K) Lignin auto-fluorescence in bottom (i) and middle (ii) sections of 2 cm (J) and 5 cm (K) peduncles. (L) Model of peduncle development. Bowman: peduncles entirely proliferative in the first phase, followed by a second phase with distinct division, elongation, maturation and termination zones and a final hyperexpansion phase in the basal peduncle associated with mitotic retreat. Zeo1.b: peduncle initiation is delayed, phase progression and growth in the coupled proliferation-expansion phase are slower, and the final hyperexpansion phase is absent. Bw, Bowman; c, collar; DZ, division zone; e, epidermis; EMZ, expansion-maturation transition zone; EZ, expansion zone; fl, flag leaf; la, central lacuna; MZ, maturation zone; n, node; p, peduncle; pa, parenchyma; pc, chlorenchyma; TZ, termination zone; v, vasculature. *P<0.05 (Student's t-test). Scale bars: 1 mm (A); 100 µm (B-E,J,K). Error bars represent s.e.m.