Figure 28.
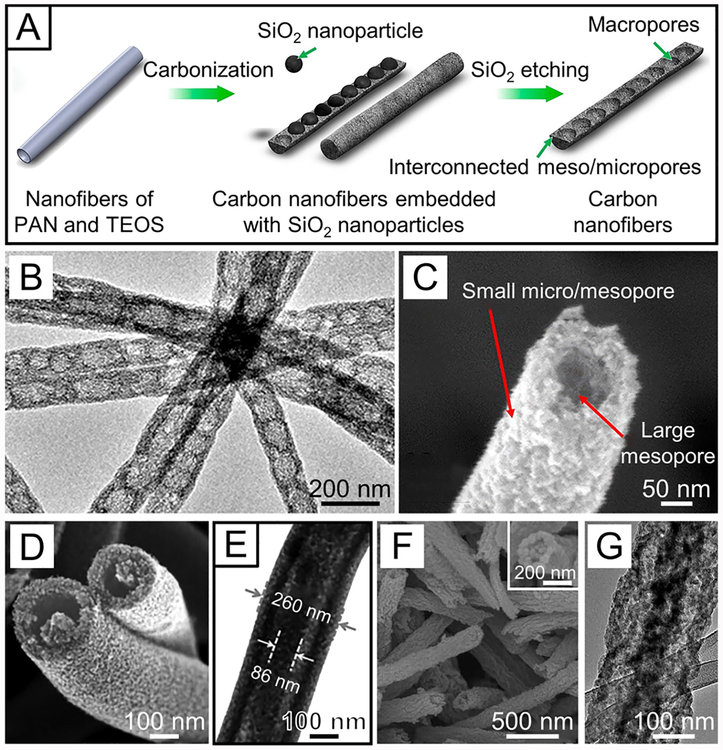
(A) Schematic showing the fabrication of hollow carbon nanofibers with a bamboo-like structure using SiO2 particles as hard templates. The electrospun nanofibers made of a blend of PAN and TEOS were carbonized at 1200 °C in an atmosphere of H2 and Ar (5:95 in volume). The ultrafine SiO2 clusters were transferred into much larger SiO2 particles through aggregation and further lined up in the core of the nanofiber. After removing the hard templates through chemical etching, hollow carbon nanofibers were produced. (B and C) TEM and SEM images of the as-obtained bamboo-like carbon nanofibers that had hollow interior together with an interconnected pore structure. (D and E) SEM and TEM images of SnO2 nanotubes with a fiber-in-tube structure. (F and G) SEM and TEM images of CoMn2O4 nanotubes with a tube-in-tube nanostructure with the inset in panel F showing a magnified SEM image. (A−C) Reprinted with permission from ref 441. Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society. (D and E) Reprinted with permission from ref 443. Copyright 2015 Wiley-VCH. (F and G) Reprinted with permission from ref 446. Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society.