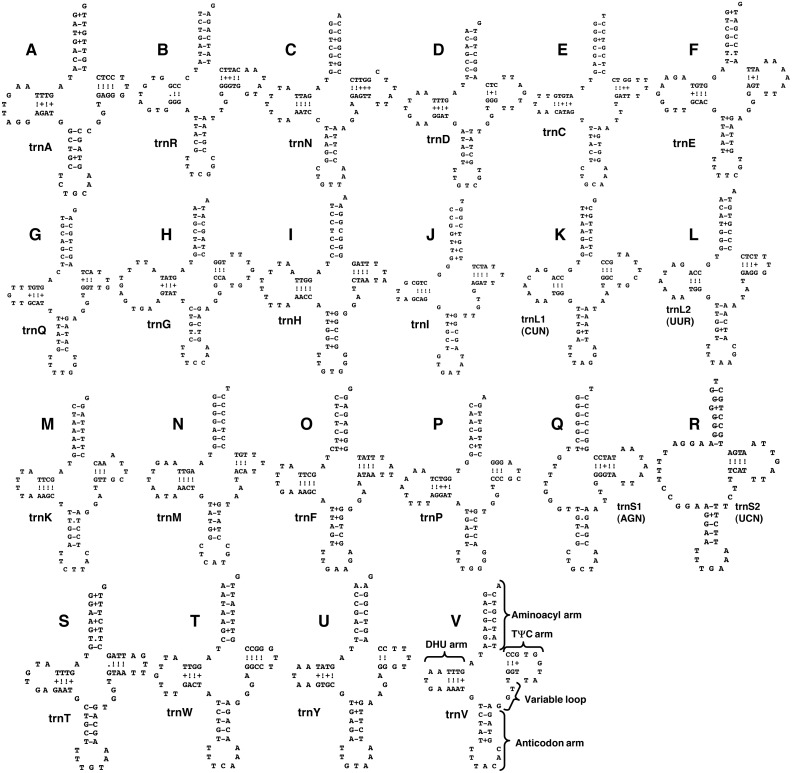
Figure 2. Drawings of predicted structure models of 22 transfer RNAs in the mitochondrial genome of Paragonimus ohirai, arranged in alphabetical order of the amino acids they specify.
Each tRNA (here abbreviated as trn) gene is named according to the one-letter amino acid abbreviation, with the exception of those specifying Serine, S1 and S2; and Leucine, L1 and L2 (L1, CUN; L2, UUR; S1, AGN; and S2, UCN); DHU arms are missing in tRNASer1(AGN) and in tRNASer2(UCN). A: trnA (Alanine); B: trnR (Arginine); C: trnN (Asparagine); D: trnD (Aspartic acid); E: trnC (Cystine); F: trnE (Glutamic acid); G: trnQ (Glutamine); H: trnG (Glycine); I: trnH (Histidine); J: trnI (Isoleucine); K: trnL1(CUN) (Leucine); L: trnL2(UUR) (Leucine); M: trnK (Lysine); N: trnM (Methionine); O: trnF (Phenylalanine); P: trnP (Proline); Q: trnS1(AGN) (Serine); R: trnS2(UCN) (Serine); S: trnT (Threonine); T: trnW (Tryptophan); U: trnY (Tyrosine); V: trnV (Valine). Names of structural components of a tRNA gene are indicated in the tRNAVal structure.