Fig. 1. Gene-wide summary measures of constraint are prone to overstating and understating constraint within specific regions of protein-coding genes.
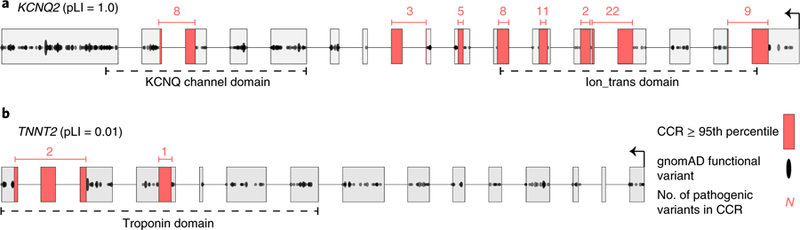
a, KCNQ2 has the highest possible pLI score of 1.0, yet there are entire exons (for example, the leftmost exon) with many protein-changing variants, indicating they are under minimal constraint. Highly constrained (that is, in the 95th percentile or higher, as described in the text) CCRs highlighted in red are devoid of protein-changing variation in gnomAD. b, In contrast, TNNT2, which regulates muscle contraction and has been implicated in familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy60, has a very low pLI of 0.01. However, there are focal regions lacking protein-changing variation, indicating a high degree of local constraint. Numbers above each CCR reflect the number of ClinVar pathogenic variants in each CCR and illustrate that CCRs often coincide with known disease loci.
