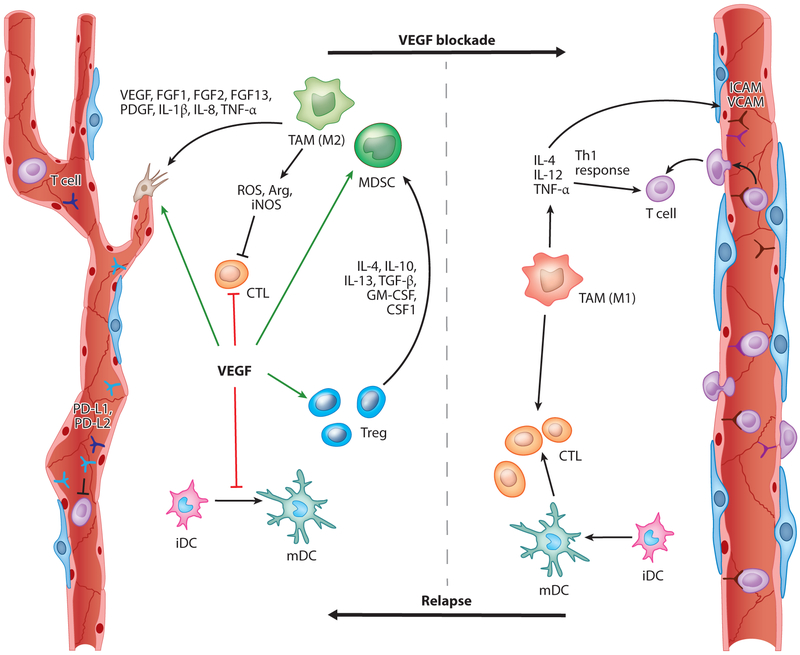
Figure 1.
VEGF/VEGFR signaling controls angiogenesis and tumor immunity. VEGF facilitates several aspects of vessel formation and also promotes immunosuppression by acting on different cell types. In endothelial cells, VEGF inhibits the expression of the T cell adhesion molecules VCAM and ICAM and induces expression of the PD-1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 that interact with PD-1 onT cells, resulting in reduced T cell proliferation and effector function. VEGF also directly impairs DC maturation and induces PD-L1 expression on mature DCs. It inhibits the proliferation and effector function of CTLs but induces the proliferation of Tregs. Tregs in turn recruit MDSCs and TAMs, which produce ROS, iNOS, and Arg to suppress T cell proliferation, viability, and activity. In contrast, inhibition of VEGF signaling enables enhanced T cell infiltration due to vessel normalization accompanied with an increase of ICAM and VCAM, which enhances DC maturation and thus provides more intratumoral effector T cells. VEGF/VEGFR blockade also increases the presence of Th1/M1-polarized myeloid cells (e.g., macrophages, neutrophils). Taken together, anti-VEGF therapy should promote an antitumor response by affecting the vasculature and the immune system. Continuous vessel pruning, however, induces hypoxic areas that drive the recruitment and polarization of immunosuppressive and angiogenic myeloid cells. Abbreviations: Arg, arginase; CSF1, colony-stimulating factor 1; CTL, cytotoxic T cell; DC, dendritic cell; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; G- or M-MDSC, granulocytic or monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; iDC, immature DC; IL, interleukin; iNOS, nitric oxide synthase; mDC, mature DC; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; PD-L1/2, programmed death-ligand 1/2; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta; Th1, T helper 1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; Treg, regulatory T cell; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, VEGF receptor.