Figure 1.
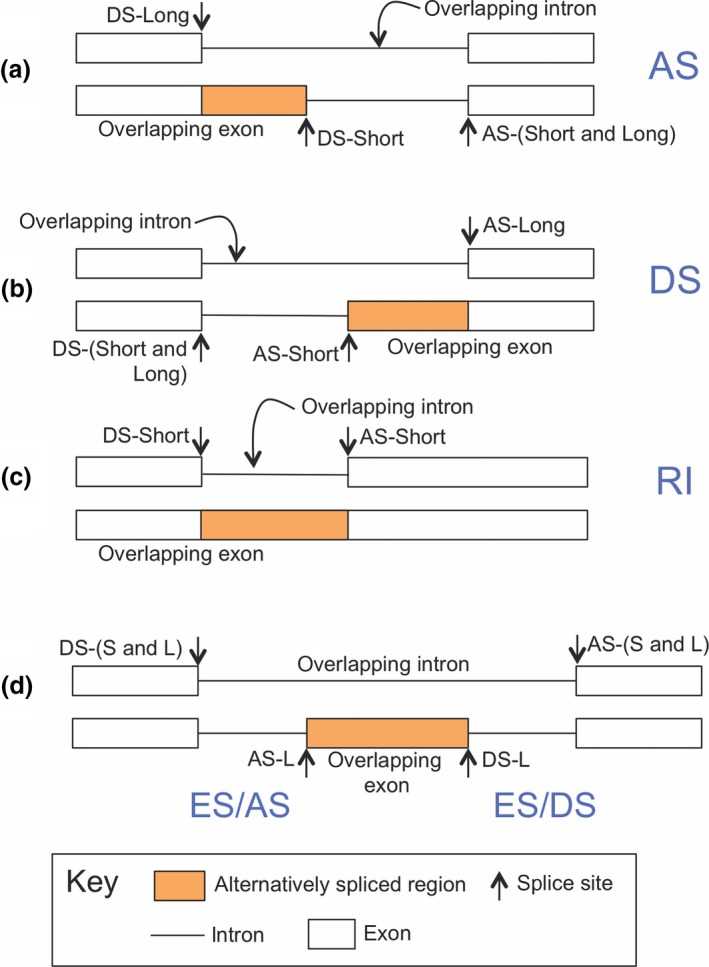
Alternative splicing annotation. The overlap between an intron in one gene model and an exon in another gene model defines an alternatively spliced region. Arrows indicate splice sites, named AS for acceptor site and DS for donor site. Use of sites named AS‐L or DS‐L causes inclusion of the differentially spliced region, generating the longer (L) form. Similarly, DS‐S and AS‐S refer to sites that exclude the differentially spliced region and generate the shorter (S) form. (a) Alternative donor sites, in which the U2 snRNP complex forms at alternative locations on the 5′ end of introns. (b) Alternative acceptor sites, in which the U1 snRNP complex forms at alternative sites near the 3′ end of alternatively spliced introns. (c) Alternatively spliced intron, in which a donor/acceptor site pairing can either be used or not used, forming a retained intron (RI). (d) Alternatively spliced, skipped exon. In exon skipping, alternative splicing involves four sites, indicated by DS‐S/L, AS‐L, DS‐L, and SD‐S/L. Exon inclusion requires assembly of two spliceosome complexes linking DS‐S/L with AS‐L and DS‐L with AS‐S/L, while exon skipping requires linking DS‐S/L and AS‐S/L only
