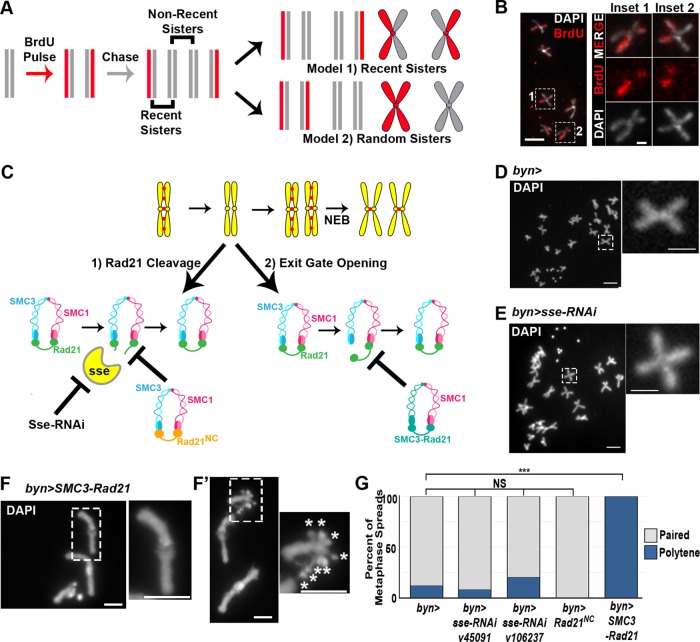
FIGURE 3:
Cohesin exit gate opening is required for SIRS. (A) Model of BrdU labeling scheme in papillar cells. Vertical lines, DNA strands. X-shapes, chromatids. Gray, unlabeled DNA, red, BrdU labeled DNA. If papillar chromosomes are composed of recent sisters, then each chromosome would have one labeled chromatid and one unlabeled chromatid (model 1). If sister chromatids are arranged randomly at metaphase, then chromosomes within the same cell would be composed of labeled and unlabeled chromosomes (model 2). Also see Materials and Methods. (B) Representative group of labeled papillar chromosomes. DAPI (DNA, white), BrdU, red. Insets, close ups of 2 chromosomes. Inset locations indicated by hatched rectangles in low magnification image for all panels in this figure. (C) Model depicting when we hypothesize cohesins are removed in papillar cells and two potential mechanisms: exit gate opening and Rad21 cleavage. Experimental methods to block these two mechanisms are shown. (D–F) Representative metaphase chromosome spreads of papillar cells. (D) byn>gal4 control. (E) byn>gal4 plus separase-RNAi driven throughout development. (F) byn>gal4 plus SMC3-Rad21 driven throughout development. Asterisk denotes X-chromosome centromeres. (G) Quantification of percentage of metaphase spreads in each class of the indicated genotypes. From left to right, N = 17, 64, 10, 8, 10 cells per genotype.