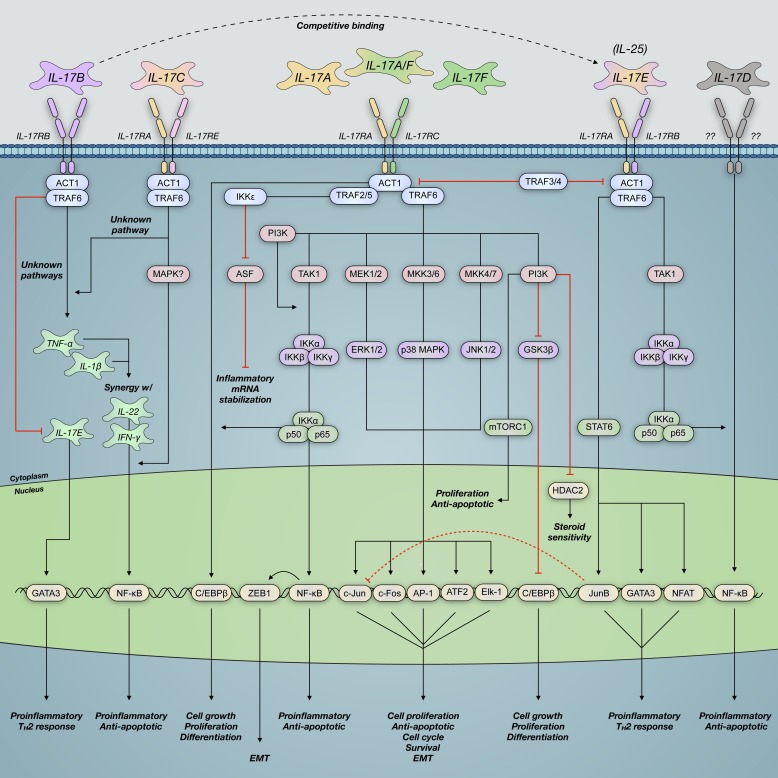
Fig. 3.
IL-17 family cytokines signal through heterodimeric IL-17 surface receptor subunits. This results in NF-κB activator (ACT)/TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) recruitment and activation of downstream effectors that impact gene transcription airway functionality. IL-17A binds its cognate IL-17 receptor A and C (IL-17RA/C) complex and activates mitogen-associated protein kinase (MAPK), phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PI3K), and nuclear factor-κ-light chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling pathways. These pathways contribute to altered airway smooth muscle function, airway remodeling, and development of symptoms consistent with severe asthma. Although other IL-17 cytokines signal via similar pathways, their mechanisms and functions within the asthmatic airway remain poorly characterized compared with those of IL-17A. AP-1, transcription factor AP-1; ASF, arginine- and serine-rich splicing factor; ATF2, cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-2; C/EBPβ, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-β; Elk-1, E26 transformation-specific (ETS) domain-containing protein Elk-1; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; GATA3, trans-acting T cell-specific transcription factor GATA-3; HDAC2, histone deacetylase 2; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; TAK1, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-activated kinase 1; TH2, T helper 2; w/, with; ZEB1, zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1.