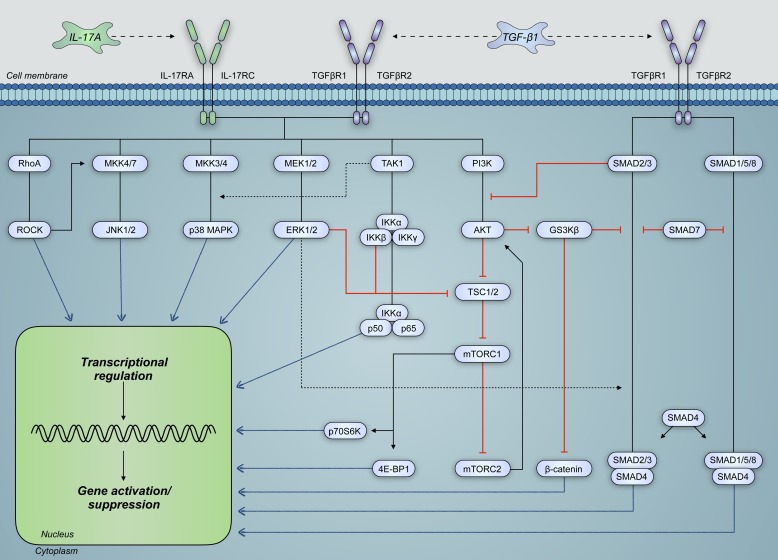
Fig. 8.
IL-17A and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) share significant cross talk in the regulation and activation of signaling pathways pertinent to structural airway cell function. These signaling pathways, which are intricately connected, can modulate the activity of one another such that overall transcriptional regulation is altered. Moreover, TGF-β1 signaling activates signal transducer mothers against decapentaplegic homolog (SMAD) pathways, which can interact with IL-17A-activated pathways to modulate gene expression. Such pathways include those of Ras homolog gene family, member A (RhoA), mitogen-activate protein kinases (MAPKs), and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PI3K). 4E-BP1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein-1; GS3Kβ, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; IL-17RA and IL-17RC, IL-17 receptors A and C, respectively; mTORC, mammalian target of rapamycin complex; p70S6K, ribosomal protein S6 kinase β-1; ROCK, Rho-associated protein kinase; TAK1, TGF-β-activated kinase 1; TGFBR, TGF-β receptor; TSC, tuberous sclerosis protein.