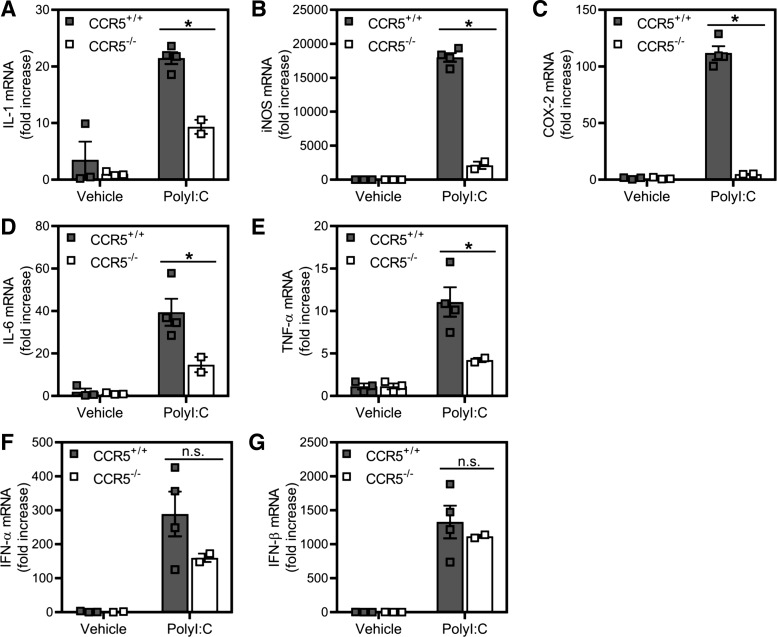
Fig. 8.
Effects of poly(inosinic:cytidylic) acid [poly(I:C)] administration on inflammatory gene expression in C-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5)-deficient (CCR5−/−) and CCR5+/+ mice. A–G: macrophages, harvested from CCR5+/+ and CCR5−/− mice 6 h after intraperitoneal administration of poly(I:C) (100 µg/mouse) or saline, were lysed, and total RNA was isolated for determination of inflammatory (A–E) and type I IFN mRNA (F and G) gene accumulation by real-time PCR. COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; iNOS, nitric oxide synthase. Results are means ± SE of 2–4 individual mice per condition. *P < 0.05.