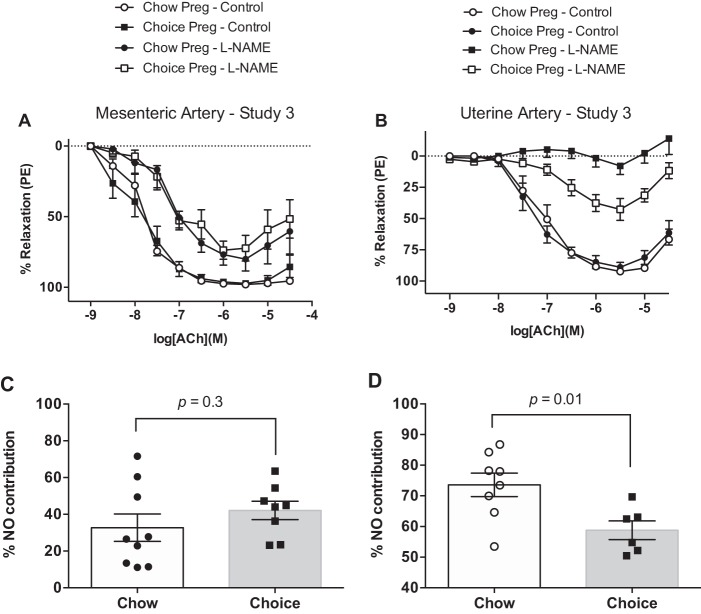
Fig. 9.
Concentration-response curves to acetylcholine (ACh) in the presence and absence of NG-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester [l-NAME; nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor] in mesenteric (A) and uterine (B) arteries from pregnant rats in study 2. Cumulative effect of ACh in the presence and absence of l-NAME was quantified as area under the curve (AUC) for mesenteric (C) and uterine (D) arteries. NO contribution was defined as the difference between ACh AUC and ACh + l-NAME AUC. There were no group differences in mesenteric and uterine artery responses to ACh, but choice diet reduced NO contribution to ACh-induced relaxation in uterine arteries. Data are means ± SE (A and C: n = 8 rats/group; B and D: n = 8 chow rats and n = 6 choice rats). Student’s t-test.