Figure 3.
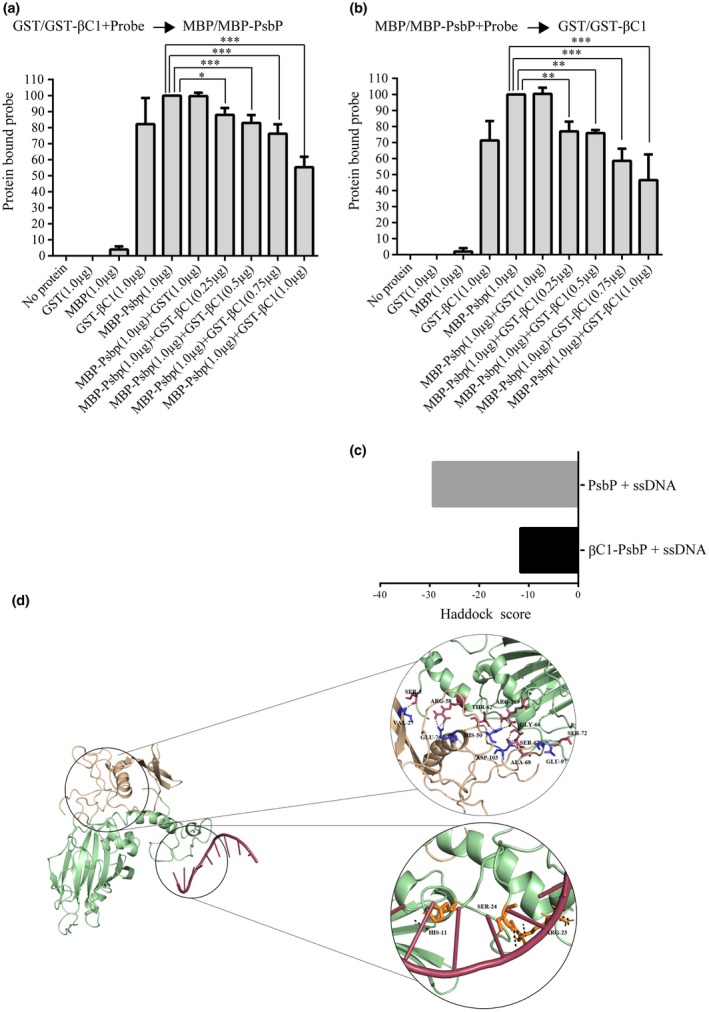
βC1 interferes with PsbP binding to viral DNA. (a) Protein competitive EMSA experiment was performed by incubating MBP‐PsbP protein with DNA‐probe pre‐incubated with increasing concentration of GST‐βC1 protein. (b) Protein competitive EMSA experiment was performed by addition of increasing concentration of GST‐βC1 protein to DNA‐probe pre‐incubated with MBP‐PsbP protein. Purified GST protein was used as negative control. The 32p‐labelled single‐stranded oligonucleotide substrate from the SCR region of betasatellite (1303 nt–1326 nt) was used as DNA‐probe. The amount of protein bound DNA was quantified using the ImageJ software and plotted using the Graph Pad Prism 6 software. Asterisks indicate reactions in which amount of protein bound DNA was significantly decreased compared with the amount of protein bound DNA in the reaction with PsbP (considered as 100%). (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001) as determined by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test by analysis of variance (ANOVA). The values are mean of the per cent of protein bound DNA from three independent experiments. (c) In silico docking of ssDNA (located at positions 1303 to 1326 in the betasatellite genome) with PsbP and PsbP‐βC1 complex. (d) In silico docking to identify potential residues of PsbP that interacts with either βC1 protein or ssDNA.
