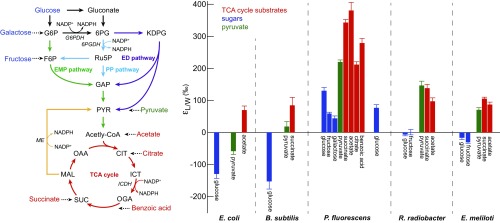
Fig. 1.
(Left) Schematic representation of the central metabolic pathways that are involved in glucose catabolism in aerobic heterotrophs—namely, the EMP pathway (green), the PP pathway (light blue), the ED pathway (violet), and the TCA cycle (red). The major NADPH-generating reactions are highlighted (11). The dehydrogenase enzymes that catalyze these reactions are G6PDH, 6PGDH, ICDH, and ME (yellow). For simplicity, not all reactions and intermediates are shown. (Right) Summary of lipid values from E. coli, B. subtilis, P. fluorescens, R. radiobacter, and E. meliloti grown on different sugars, TCA cycle intermediates, pyruvate, and benzoic acid. values are calculated from the abundance-weighted mean H values of fatty acids and that of culture medium. Error bars represent the corresponding abundance-weighted SDs. Typical replicate precision is ‰, larger than typical analytical uncertainties of ‰.