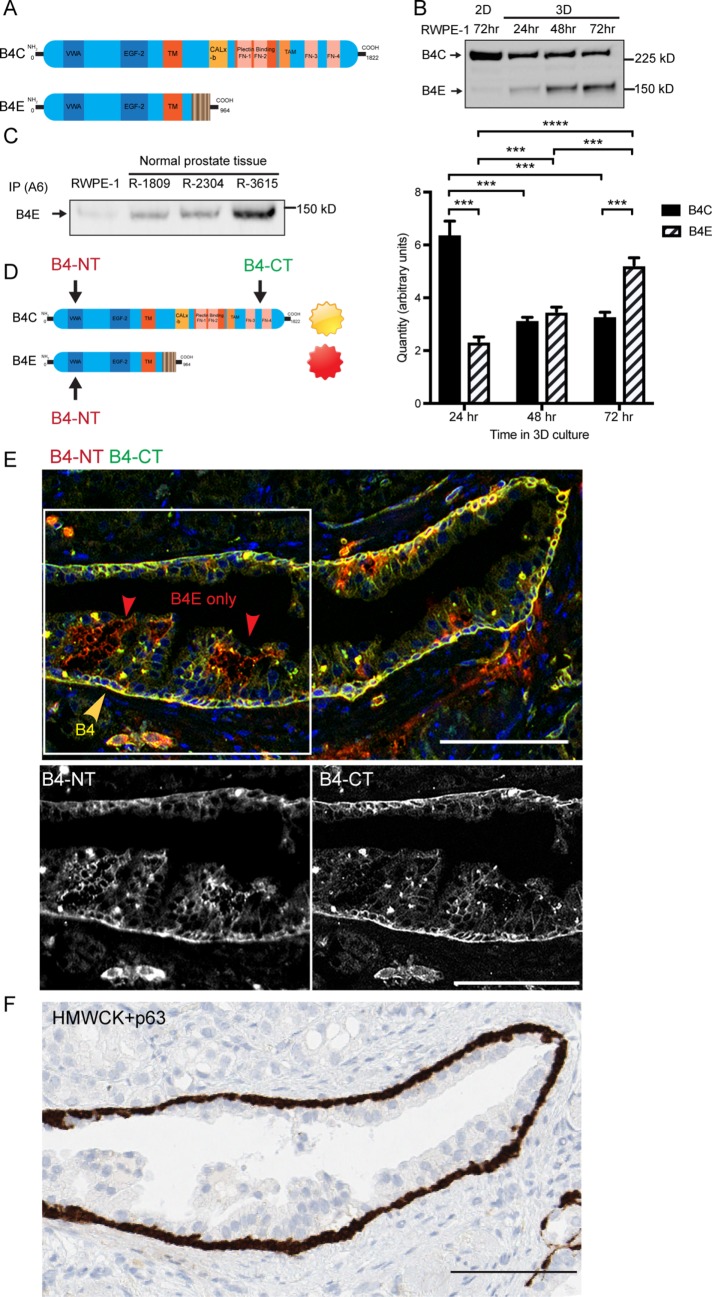
FIGURE 1:
Integrin β4E and integrin β4C are present within human prostate cell lines and patient-derived tissue, and β4E is distributed within the luminal cell compartment. (A) Schematic of the different functional domains of integrin β4C and integrin β4E variants. (B) Integrin β4 heterodimers (B4C, B4E) can be detected in normal basal cells (RWPE-1) in 2D culture after 72 h or in 3D cultures after 24, 48, or 72 h by immunoprecipitation of α6 integrin, followed by Western blot protein analysis. Quantities of β4C or β4E mRNA specific for each isoform were detected by qRT-PCR using isoform-specific primers. Data are shown as means ± SD, n = 3. Statistical comparison was done by nonparametric, two-tailed Student’s t test (***, p < 0.005). (C) Immunoprecipitation of α6 integrin (IP A6) and retrieval of α6β4E heterodimer from normal prostate tissue. (D) The strategy and location of the epitopes of the β4 N-terminus antibody (B4-NT) and β4C-terminus antibody (B4-CT) were used to detect different β4 variants in human prostate tissue. (E) Epifluorescence images show the basal distribution of the β4C isoform (yellow arrow) and the β4E isoform (red arrow). The color channels for the boxed region were separated to show the distribution of β4 N-terminus antibody (B4-NT) or the β4 C-terminus antibody (B4-CT). The distribution of HMWCK and p63 detects the basal cell layer (F, brown) within a serial section of the same gland shown in E. Scale bars: 100 microns.