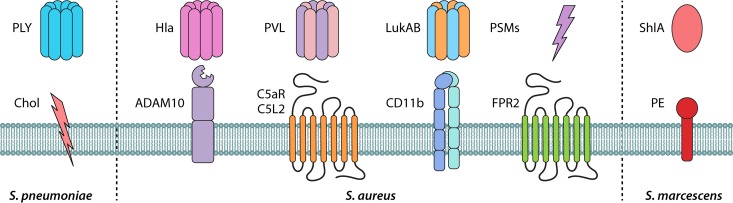
FIG 1.
Pore-forming toxins and their receptors in pneumonia. Staphylococcus aureus and other bacterial toxins involved in bacterial pneumonia are shown. S. aureus alpha-toxin (Hla), Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL), leukotoxin AB (LukAB), and phenol-soluble modulins (PSMs) bind to their corresponding membrane receptors to mediate damage and inflammation. C5aR and C5L2, complement component 5a receptors; CD11b, subunit that forms the integrin αMβ2, also known as macrophage-1 antigen (Mac-1) or complement receptor 3 (CR3); ADAM10, disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 10; FPR2, formyl peptide receptor 2. PSMs and Hla can target both human and mouse cells, while PVL and LukAB are human-specific toxins. Streptococcus pneumoniae cytolysin pneumolysin (PLY) and Serratia marcescens toxin ShlA both bind to components of the membrane, i.e., cholesterol (Chol) or phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), respectively, to induce damage and inflammation.