Figure 4.
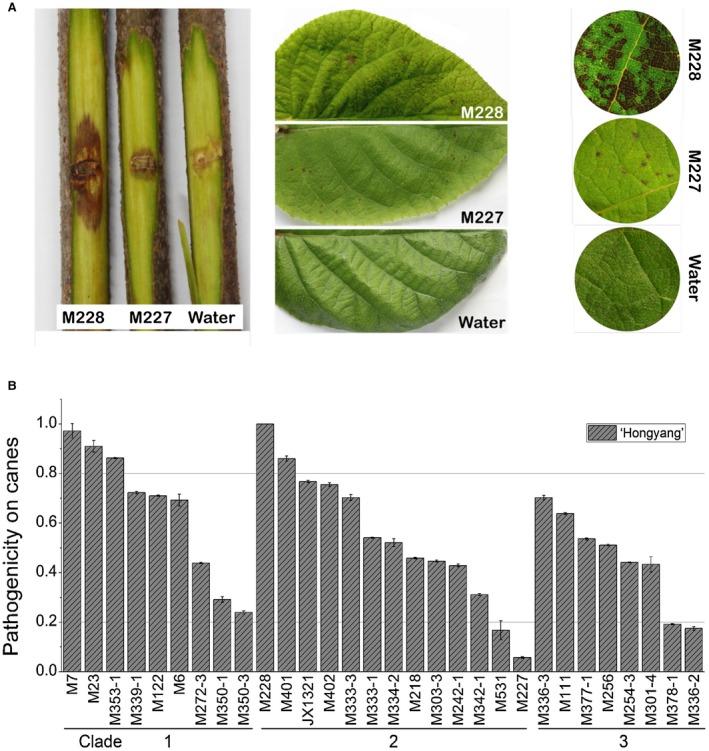
Reliable indoor bioassay methods to test the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae (Psa) strains. (A) Three indoor bioassay methods were developed: 1) wound inoculation on detached dormant kiwifruit canes with 108 CFU/mL bacteria, 2) spraying the inoculate on unwounded kiwifruit leaves with 106 CFU/mL bacteria, 3) vacuum infiltration inoculation on leaf discs with 104 CFU/mL bacteria. The three methods showed very similar results when used to test the pathogenicity of the high‐virulent Psa strain M228 and a low‐virulent Psa strain M227. (B) Diverse pathogenicity of the Psa biovar 3 (Psa3) strains on kiwifruit in Shaanxi Province, China. The pathogenicity patterns of 30 Psa3 strains from Shaanxi Province were obtained by wound inoculation on detached dormant woody canes of Actinidia chinensis var. chinensis ‘Hongyang’. A variation in pathogenicity was observed amongst strains within each genetically monomorphic clade. The lesion length measured at 15 day post‐inoculation (dpi) of each strain was normalized to that of Psa3 strain M228. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results.
