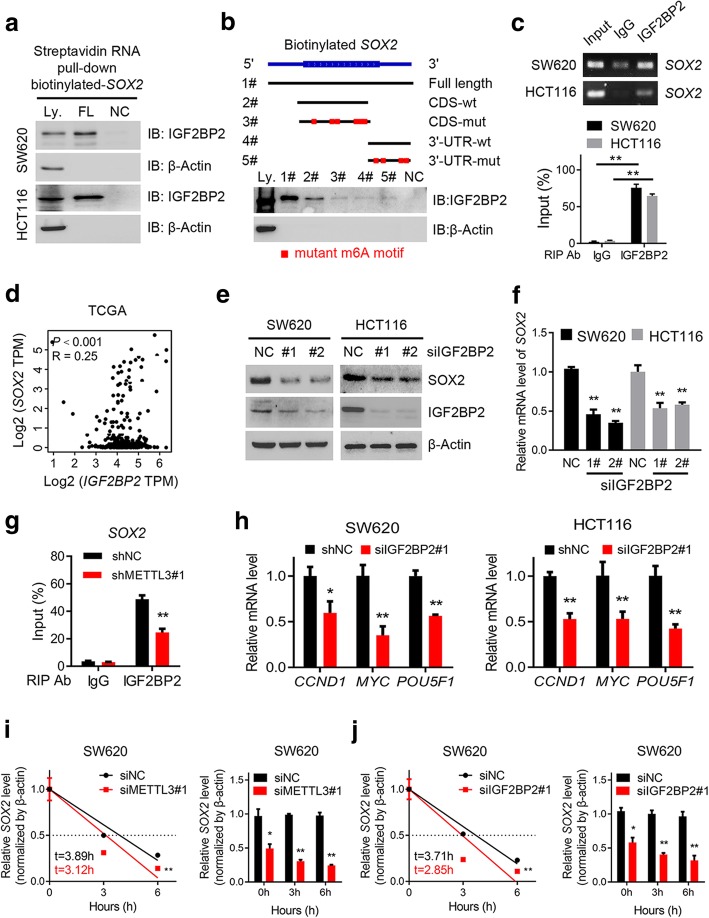
Fig. 5.
IGF2BP2 enhances SOX2 mRNA stability via an m6A-dependent manner. a, Immunoblotting of IGF2BP2 after RNA pull down assay with cell lysate (Ly.), full-length biotinylated-SOX2 (FL), and beads only (NC) in SW620 and HCT116 cells. b, Immunoblotting of IGF2BP2 with cell lysate (Ly.), full-length biotinylated-SOX2 (#1), the SOX2 CDS region with or without m6A motif mutation (#2, #3), the SOX2 3′-UTR region with or without m6A motif mutation (#4, #5), and beads only (NC) in SW620 cells. c, Agarose electrophoresis and real-time PCR analysis of RIP assays in CRC cells showing the direct binding between the IGF2BP2 protein and SOX2 mRNA. d, Correlation between IGF2BP2 and SOX2 expression in TCGA database for COAD, analyzed with the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) online analysis tool (http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/). e, Immunoblotting of SOX2 after IGF2BP2 inhibition in SW620 and HCT116 cells. f, Real-time PCR analysis of SOX2 after IGF2BP2 inhibition in SW620 and HCT116 cells. g, RIP-qPCR showing the enrichment of SOX2 in SW620 after METTL3 inhibition. h, Real-time PCR analysis of SOX2 downstream genes after IGF2BP2 inhibition in SW620 and HCT116 cells. i-j, The decay rate of mRNA and qPCR analysis of SOX2 at the indicated times after actinomycin D (5 μg/ml) treatment in SW620 cells after METTL3 inhibition (left), and in SW620 cells after IGF2BP2 inhibition (right). The data in c, g, h, i and j are presented as the mean ± SDs (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). β-Actin and an IgG antibody was used as the negative control. The relative expression level was normalized by β-Actin. The relative SOX2 enrichment in the RIP assay was normalized by input