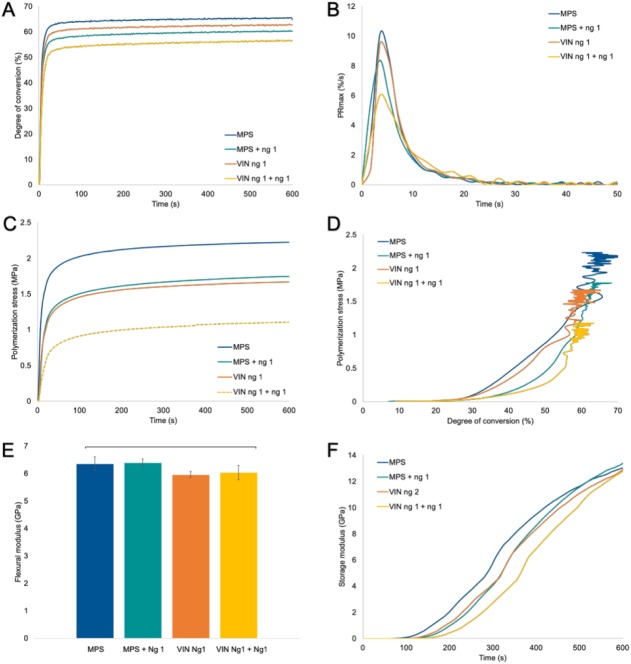
Figure 3.
Conversion and property development for composite formulations. (A) Real-time polymerization shows a slightly lower degree of conversion for the different composite systems as compared with the MPS control composite, (B) while the polymerization rate is slower in systems with free nanogel addition but similar to control for nanogel-based fillers. (C) Composite polymerization stress profiles demonstrate a reduction in polymerization stress by about 20% for free nanogel addition and nanogel-based fillers but a 50% reduction when both strategies are combined. (D) The MPS control composite and nanogel-based fillers present stress development at lower degrees of conversion than the systems with free nanogel loading. (E) The flexural modulus is similar to control for all experimental materials. Real-time elastic modulus development during polymerization shows an early increase in modulus for MPS control, followed by nanogel-based fillers and free nanogel addition with the latest modulus rise observed when both approaches are combined. Values are presented as mean ± SD. (F) Notably, the final storage modulus is similar for all groups. MPS, γ-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane; Ng, nanogel; VIN, trimethoxyvinylsilane.