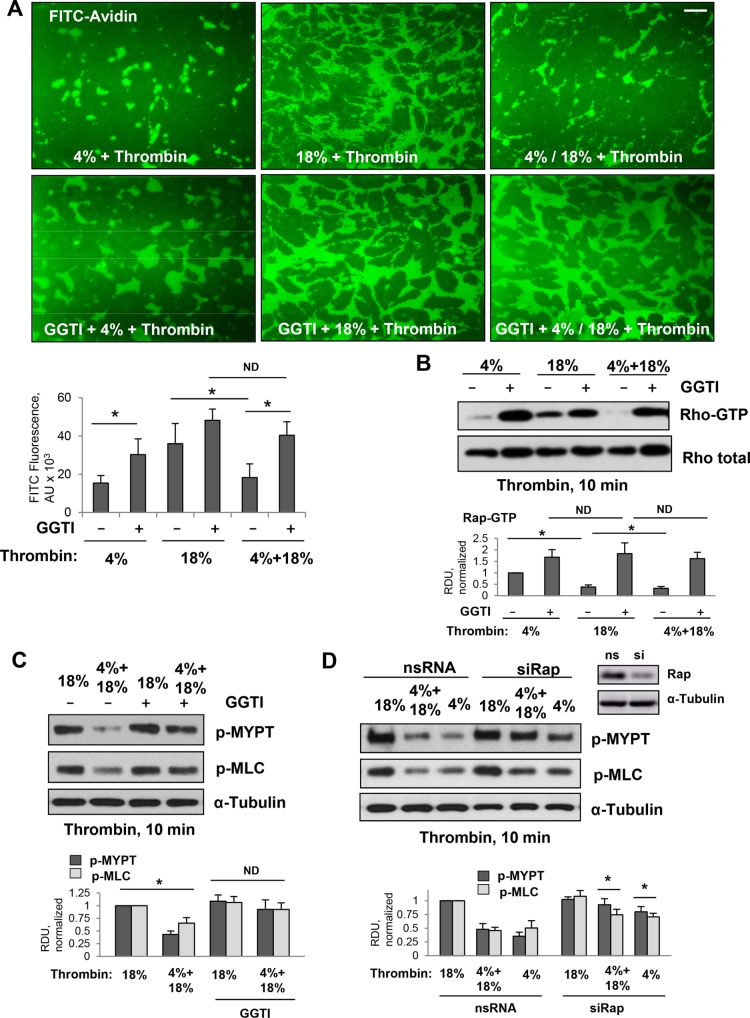
FIGURE 4:
Effects of pharmacologic and molecular inhibition of Rap1 on down-regulation of Rho signaling caused by thrombin and high-magnitude CS in ECs preconditioned at 4% CS. Pulmonary ECs were exposed to 4% CS or 18% CS for 6 h, or to 3-h 4% CS switched to 3-h 18% CS. Thrombin (0.05 U/ml) was added for the last 10 min of CS experiment. Rap1 inhibitor (GGT-298, 15 µM) was added for 30 min before the 18% CS or before switching to 18% CS. (A) Visualization and quantitative analysis of FITC-avidin binding to the bottoms of the plates with CS-stimulated EC monolayers. Rap1 inhibitor attenuated 4% CS-induced protection of EC barrier integrity as detected by XPerT permeability assay. Bar = 20 µm. (B) Inhibition of Rap1 by pretreatment with GGTI-298 abolished down-regulation of RhoA activity caused by EC exposure to 4% CS. (C) Rap1 inhibitor attenuated suppression of RhoA-dependent phosphorylation of MYPT and MLC caused by 4% CS preconditioning. (D) Effect of siRNA-induced Rap1 knockdown on 4% CS-induced suppression of MYPT and MLC phosphorylation caused by thrombin. Right panel shows efficiency of siRNA-induced Rap1 protein depletion. Membrane reprobing for α-tubulin was used as a normalization control. Bar graphs represent analysis of Western blot data; n = 3; *, p < 0.05 vs. nonspecific RNA.