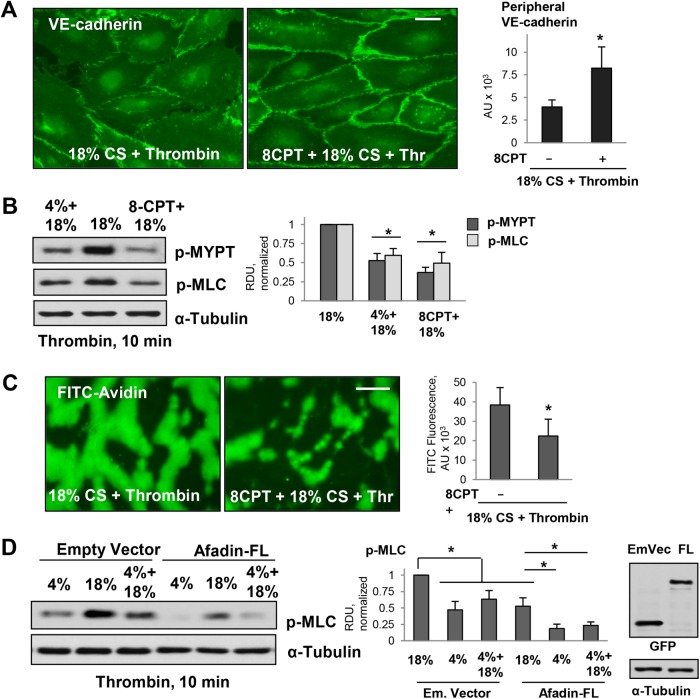
FIGURE 5:
Effects of pharmacologic Rap1 activation on EC permeability in pulmonary ECs exposed to 18% CS and thrombin. (A) Pulmonary ECs were exposed to 18% CS for 6 h with or without 8CPT pretreatment (75 µM, 30 min before 18% CS) followed by thrombin stimulation (10 min). EC monolayers were then fixed and used for immunofluorescence staining with VE-cadherin antibody. Bar = 5 µm. Bar graph represents quantitative analysis of peripheral VE-cadherin signal intensity expressed as mean ± SD; n = 4 independent experiments; *, p < 0.05. (B) 18% CS-induced increase of pMYPT and pMLC levels was inhibited by 8CPT pretreatment. Bar graphs represent analysis of Western blot data; n = 3; *, p < 0.05 vs. 18% CS. (C) 18% CS-induced increase in EC permeability was inhibited by 8CPT pretreatment as detected by XPerT permeability assay; n = 4 independent experiments; *, p < 0.05. Bar = 10 µm. (D) Ectopic expression of afadin attenuated thrombin-induced MLC phosphorylation in ECs exposed to 4 and 18% CS. The ECs were transfected with empty vector or afadin plasmid (WT) 48 h before the CS stimulation. Right panel depicts protein expression of recombinant GFP-tagged afadin in pulmonary ECs. Membrane reprobing for α-tubulin was used as a normalization control. Bar graphs represent analysis of Western blot data; n = 3; *, p < 0.05.