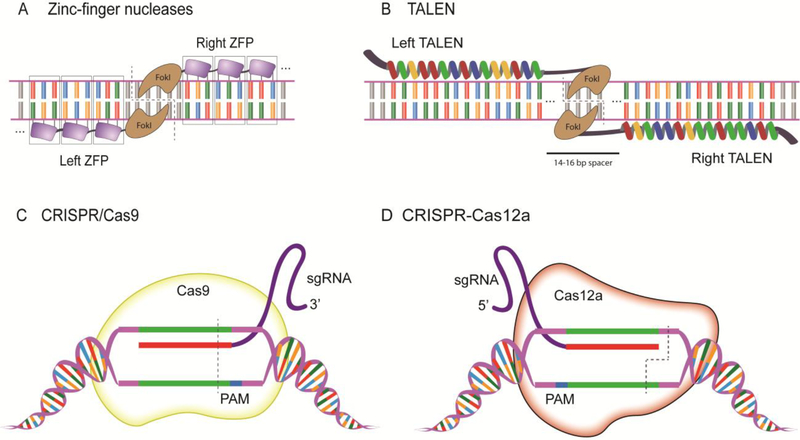
Fig 1. Established guided designer endonucleases used in zebrafish.
(A) Zinc-finger nucleases recognize DNA by the fusion of 3 zinc finger recognition domains on either side of the DNA, specifically binding an 18nt region in this example, and the fused FokI dimerizes and catalyzes cleavage of the DNA. (B) An illustrative 15 repeat TALEN binds on either strand of the DNA separated by a spacer region, and the DSB occurs around the halfway point in the spacer region where the FokI domains dimerize.(C) SpCas9 recognizes the target sequence with the assistance of the sgRNA next to the 3’ PAM sequence and induces a double stranded break 3 base pairs 5’ from the PAM. (D) Cas12a recognizes the target sequence with the assistance of the sgRNA next to the 5’ TTTN PAM sequence and cleaves the DNA at the 18th base on the non-targeted strand and after the 23rd base on the targeted strand to create sticky ends at the DSB. (see text)