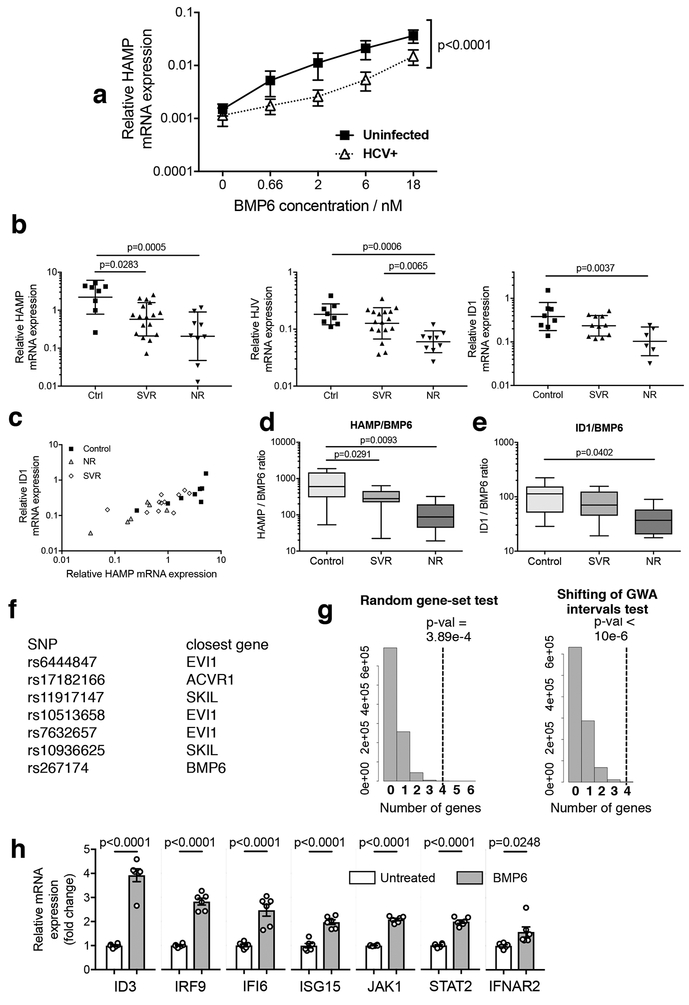
Figure 1:
HCV–BMP pathway interactions decrease hepcidin and associate with therapeutic outcome a Uninfected or HCV-infected (MOI = 0.02) Huh7.5 cells were incubated with a titration of BMP6 overnight; HAMP mRNA induction in response to BMP6 was significantly suppressed in HCV-infected cells (Mean ± SEM shown; P<0.0001: two-tailed Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test; n=6 biologically independent experiments).
b Patients with known treatment outcome (n=26 biologically independent samples) were separated by outcome (Sustained Virological Response (SVR) and Non-Responder (NR) and compared to the control group (n=8). HAMP mRNA expression was reduced in both groups compared to controls whereas HJV and ID1 were significantly reduced only in the NR group (Geometric means +/− geometric standard deviations shown; one-way ANOVA on log10-transformed data: Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test adjusted p-values are indicated.
c BMP target genes ID1 and HAMP mRNA were correlated across these three groups (Pearson correlation of log10-transformed data: r2=0.701; p<0.0001 (two-tailed); n=25 independent samples (n=8 control, n=11 SVR, n=6 NR).
d, e Ratio of expression of HAMP or ID1 to BMP6, derived to represent an ‘output-per-input’ ratio (data available from n=25 independent samples: n= 8 control; n=11 SVR;; n=6 NR). HAMP/BMP6 was significantly reduced in NRs and SVRs; ID1/BMP6 was significantly reduced in NRs (boxes indicate inter-quartile range with median; whiskers indicate range; one-way ANOVA: Tukey’s multiple comparison test adjusted p-values are indicated).
f, g BMP pathway gene enrichment is linked to HCV clearance. SNPs linked to four BMP-pathway genes (BMP6, ACVR1/ALK2, EVI1, SKIL, (f)) were in the top 66 GWA intervals associated with differential clearance of HCV (Ge et al., 2009). g The frequency of four genes (black dotted line) from a million randomly generated gene-sets of similar size to the BMP pathway occurring in the 66 GWA intervals identified by Ge et al (Random gene-set, left), or of four BMP pathway genes occurring in a million randomly generated sets of 66 GWA intervals (Shifting of GWA intervals, right), was determined against randomized backgrounds (grey histograms), as discussed in detail in Supplementary Methods.
h Changes in expression of the type I IFN pathway related genes (IFNAR2, JAK1, STAT2, IRF9, ISG15, IFI6) identified by microarray of Huh7.5 cells treated with BMP6 for 24h were confirmed by qRT-PCR; BMP target gene ID3 was measured as a positive control (n = 2 independent experiments, each run in triplicate, giving a total of 6 RNA extracts per condition; plots depict mean +/− SEM fold changes relative to untreated cells; two-tailed unpaired t-test)