Fig. 1.
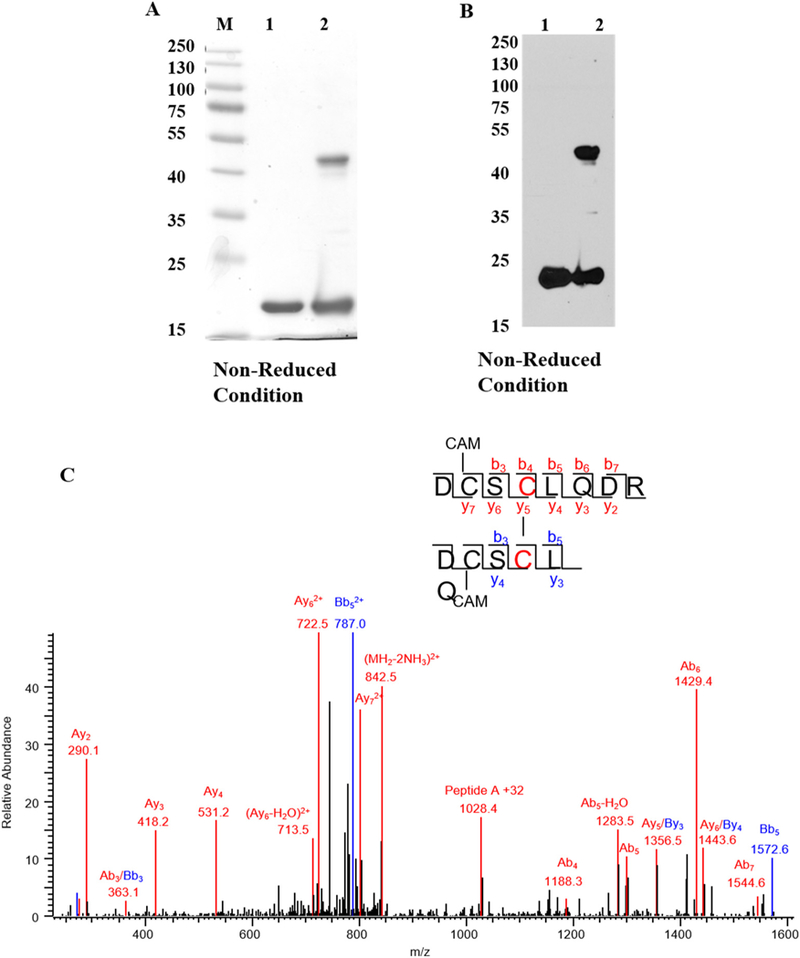
Diamide oxidation of human γD-crystallin. (A) 1 mg/ml of recombinant hγD in Chelex treated 50mMK + /PO4 buffer pH 7.4 was incubated with 10 μl diamide at 37 °C for 3 h. Dimer formation was analyzed by 12% SDS-PAGE and destained overnight. The image was scanned under greyscale using Epson scanner. M-Protein marker, lane 1 -non-oxidized hγD, lane 2 -oxidized hγD. (B) Dimerization was confirmed by western blot using hγD polyclonal antibody and the blot was developed using X-ray film using ECL solution the developed film was scanned under greyscale using EPSON scanner, lane 1 -non-oxidized hγD, lane 2 -oxidized hγD. For both SDS-PAGE and western blot samples were derived from the same experiment and processed in parallel. (C) Tandem mass spectrum of disulfide formation between Cys111-Cys111 in hγD dimer. Both Cys 109 residues are carbami-domethylated. The series b and y ions with A and B represent the fragment ion from peptide DCSCLQDR (A) and DCSCLQ (B), respectively. The precursor ion m/z is 859.8151 (2+).
