Figure 5. DC/AML fusion vaccine prevents engraftment and increases leukemia-specific immunity in murine syngeneic AML model.
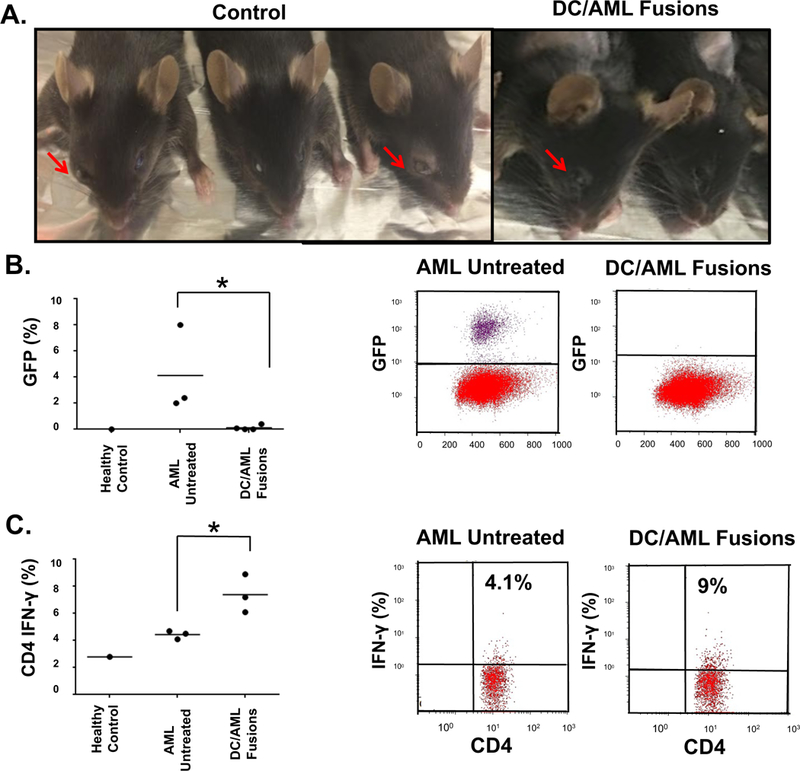
DCs were generated from the BM cells harvested from femurs of C57BL/6J black mice. BM cells were cultured in the presence of IL-4 and GM-CSF for 5–7 days to induce DC differentiation and maturation. To generate the fusion vaccine, the DCs were then collected and fused with GFP+ syngeneic TIB-49 AML cells in the presence of PEG. Fusion cells were identified through sorting by co-expression of CD86 and GFP. Black mice were inoculated retro-orbitally with GFP+ TIB-49 cells and 24 hours later, mice were injected subcutaneously with the sorted DC/AML fusion vaccine. Two weeks following inoculation with TIB-49 cells, control mice exhibited significant tumor growth at the injection site as opposed to mice treated with the DC/AML fusion vaccine (A). Two weeks following inoculation with TIB-49 cells, BM of the animals was harvested and examined for GFP expression. The percent of BM-infiltrating blasts (B) is depicted. Stimulation of those BM-derived cells with autologous tumor lysate as detected by intracellular IFN-γ expression is shown in (C).
