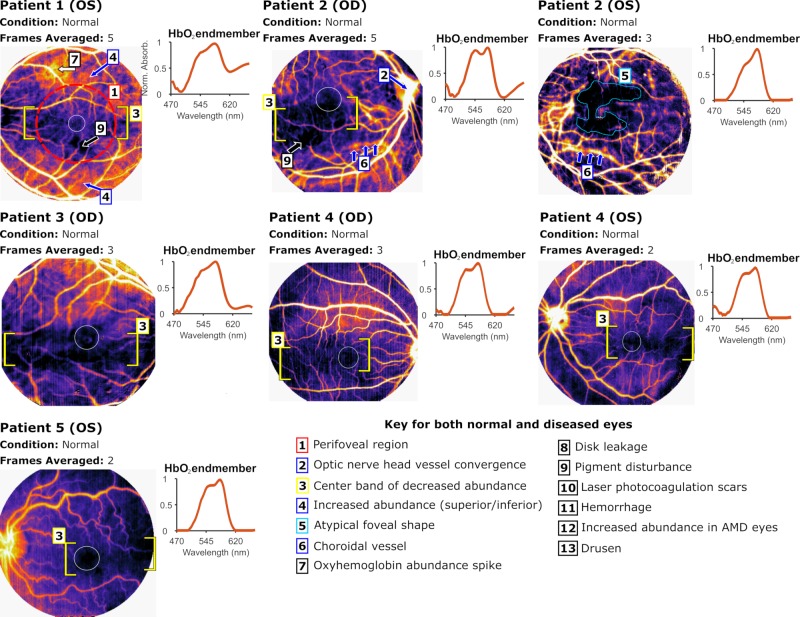
Figure 8.
HbO2 abundance maps for healthy eyes. Presented with each eye is a colormap with patient condition, number of frames (data cubes) averaged to achieve the final map, and the spectral endmember result from NNMF. The right eye map for patient 1 is not available, and the left eye map for patient 3 was excluded. Blue arrows point to unique regions of interest, white arrows correspond to localizations of increased HbO2 abundance, and black arrows point to regions devoid of unmixed HbO2 (dropout). The white circle outlines foveal boundaries as interpreted by the maps. Yellow brackets demonstrate the bounds of center bands of lower HbO2. The nasal side of the FOV exhibits large regions of HbO2 dropout in patients 4 (OD and OS), 5 (OS), and 8 (OS), pictured in Figure 9 below. Hard exudates, floaters, and pigment abnormalities appear as sharp HbO2 dropout as would be expected as these entities carry no vascular elements and hence, no HbO2.