Figure 1.
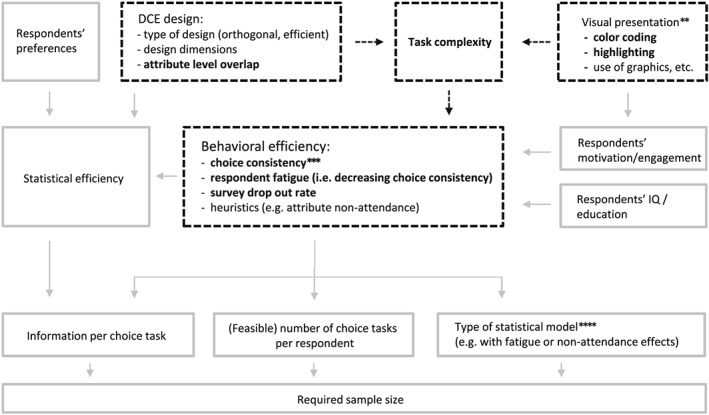
Conceptual model of the trade‐off between statistical and behavioral efficiency. The scope of analyses in this paper is indicated by the bold fonts and dashed lines and arrows. **The visual presentation can moderate the impact of task complexity on behavioral efficiency but may also affect respondents' motivation and engagement. These two pathways are not disentangled in this paper. ***Statistical efficiency is determined by (a) the DCE design, (b) the type of statistical model to be estimated, (c) respondents' preferences (i.e., relative attribute and level importances), and (d) respondents' choice consistency. The latter explains the effect of behavioral efficiency on statistical efficiency. ****Most efficient DCE designs are optimized for the standard conditional logit model, irrespective of the model actually expected to be estimated. Hence, there is (usually) no feedback loop from the type of statistical model to the DCE design. DCE: discrete choice experiment
