Figure 6.
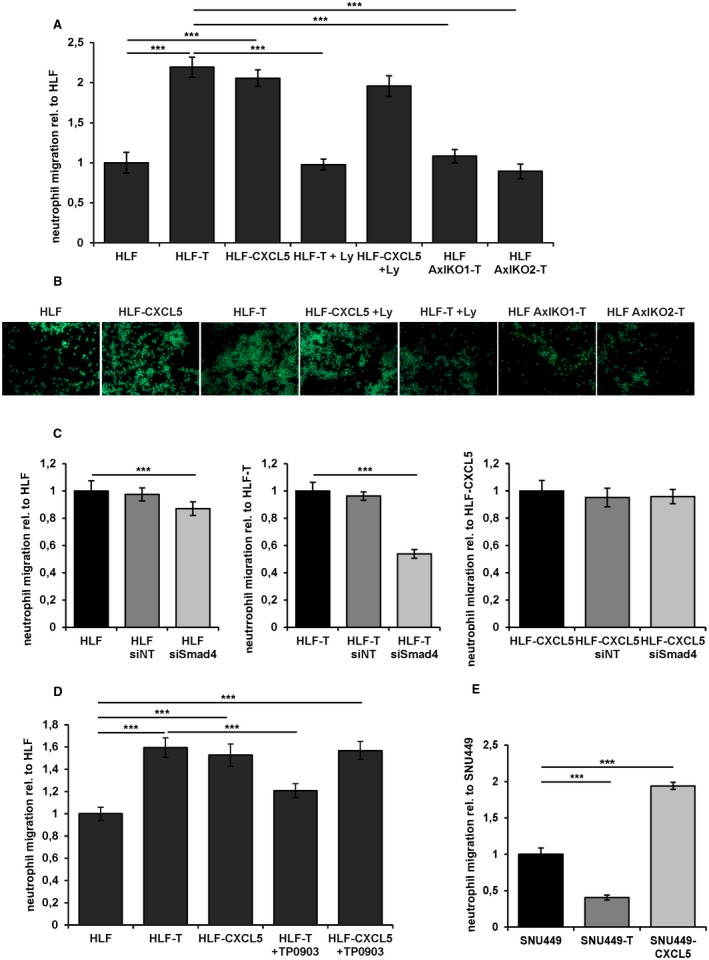
Long‐term TGF‐β treatment causes neutrophil migration. (A) Quantification of neutrophil migration as assessed by under‐agarose assay. Cell Tracker green‐labeled neutrophils were exposed to supernatants of HLF, HLF‐T, and HLF‐CXCL5 cells, those treated with 10 µM Ly for 24 hours, and long‐term TGF‐β‐treated (>10 days) HLF‐Axl‐KO1‐T and HLF‐Axl‐KO2‐T cells. (B) Representative immunofluorescence images of the under‐agarose assay shown in (A). (C) Quantification of neutrophil migration after exposure to supernatants from HLF (left panel), HLF‐T (middle panel), and HLF‐CXCL5 cells (right panel) treated with siNT or siSmad4. (D) Quantification of neutrophil migration after exposure to supernatants of HLF, HLF‐T, and HLF‐CXCL5 cells and those treated with 1 µM Axl inhibitor TP0903 for 48 hours. (E) Quantification of neutrophil migration after exposure to supernatants of SNU449, SNU449‐T, and SNU449‐CXCL5. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. ***P < 0.001.
