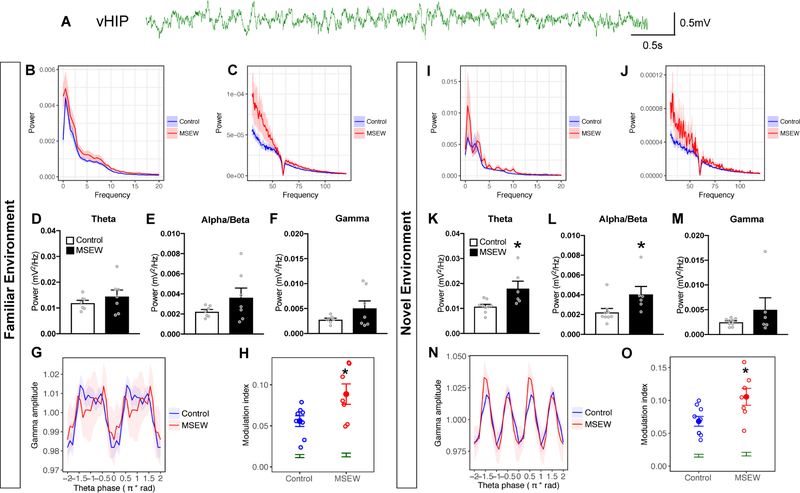
Figure 3.
(A) Raw LFP trace from the vHIP. (B,C) High and low frequency power spectra plots from MSEW mice during 10 minutes in the familiar environment (F.E). In the F.E, there were no power differences in either theta (D), alpha/beta (E) or gamma (F) power between groups. (G) Phase amplitude coupling analysis plotting normalized gamma power as a function of theta phase in the F.E (H) Analysis of theta-gamma phase amplitude coupling in the F.E. revealed that MSEW mice had significantly more modulation compared to controls. (I, J) High and low frequency power spectra plots from MSEW mice during 10 minutes in the novel environment (N.E). (K,L) In the N.E, theta and alpha/beta frequency power was significantly increased in MSEW mice compared to controls. (M) No changes in gamma power were observed between groups in the N.E. (N) Phase amplitude coupling analysis plotting normalized gamma power as a function of theta phase in the N.E. (O) Permutation tests showed significantly greater modulation above chance for both treatment conditions (green). MSEW significantly increased theta-gamma modulation relative to controls in the N.E, suggesting enhanced theta-gamma coupling in the vHIP due to early life adversity. *p<0.05