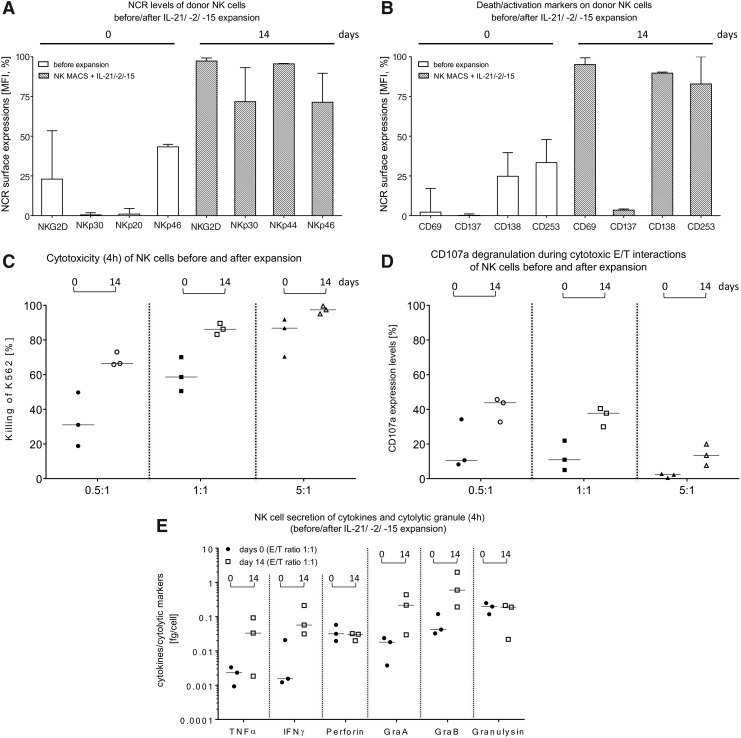
Figure 3.
Comparison of cytotoxic properties and activation markers on primary NK cells before and after the expansion process in Prodigy. IPCs (approximately 2.0–2.5 mL) were collected as indicated in Fig. 1A for analysis of NK cell-dependent cytotoxicity, CD107a degranulation, surface marker expression levels, and cytokine secretion. NK cell phenotyping of (A) NCRs (NKG2D, NKp30, NKp44, and NKp46), (B) activation markers (CD69 and CD137), and death receptors (CD178 and CD253) were analyzed by flow cytometry for 2-week-cultured NK cells compared to highly purified NK cells before the expansion period. Correspondingly, effector cell-mediated cytotoxicity (C) and CD107a degranulation rates (D) were analyzed for expanded NK cells against K562 cells at indicated effector-to-target (E/T) ratios and compared to freshly separated NK cells before starting the expansion period (day 0). (E) Secretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interferon gamma, perforin, granzyme A and B, and granulysin were determined after cytolytic reactions in supernatants of co- and mono-cultured NK and K562 cells. Medians with ranges are shown from three independent experiments performed in duplicate.