Figure 2.
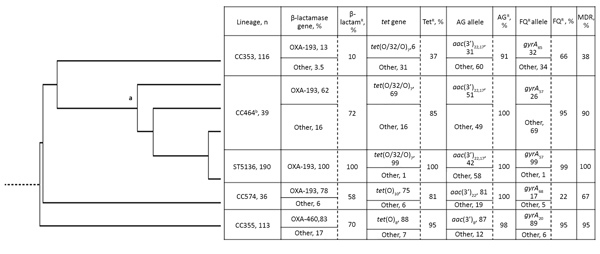
Whole-genome phylogenetic tree of Campylobacter jejuni CC464, CC353, CC574, and CC354 isolates, Scotland; a indicates CC464 root and b indicates CC464 isolates excluding ST5136. β-lactamase gene (blaOXA-61–like) indicates presence of abundant allele and other OXA genes; β-lactamR, resistant isolates (defined by −10 promoter mutation or presence of OXA-184–like gene). tet gene indicates presence of abundant tetracycline resistance allele and other alleles; TetR, tetracycline-resistant isolates. AG allele indicates presence of abundant aminoglycoside allele and other alleles in a group of strains associated at the CC level; other indicates any other aac3 resistance allele or a combination of the abundant allele along with a second aac3; AGR indicates aminoglycoside-resistant isolates. FQ allele indicates most abundant gyrA allele and other alleles that confer fluoroquinolone resistance; FQR indicates fluoroquinolone-resistant isolates. MDR is defined as resistance to >3 antimicrobial drugs. CC, clonal complex; MDR, multidrug resistant; OXA, oxacillin; R, resistant; ST, sequence type.
