Fig 1. Developmental and physiological defects in atbg1, vat1 and atbg1/vat1 mutants compared to WT.
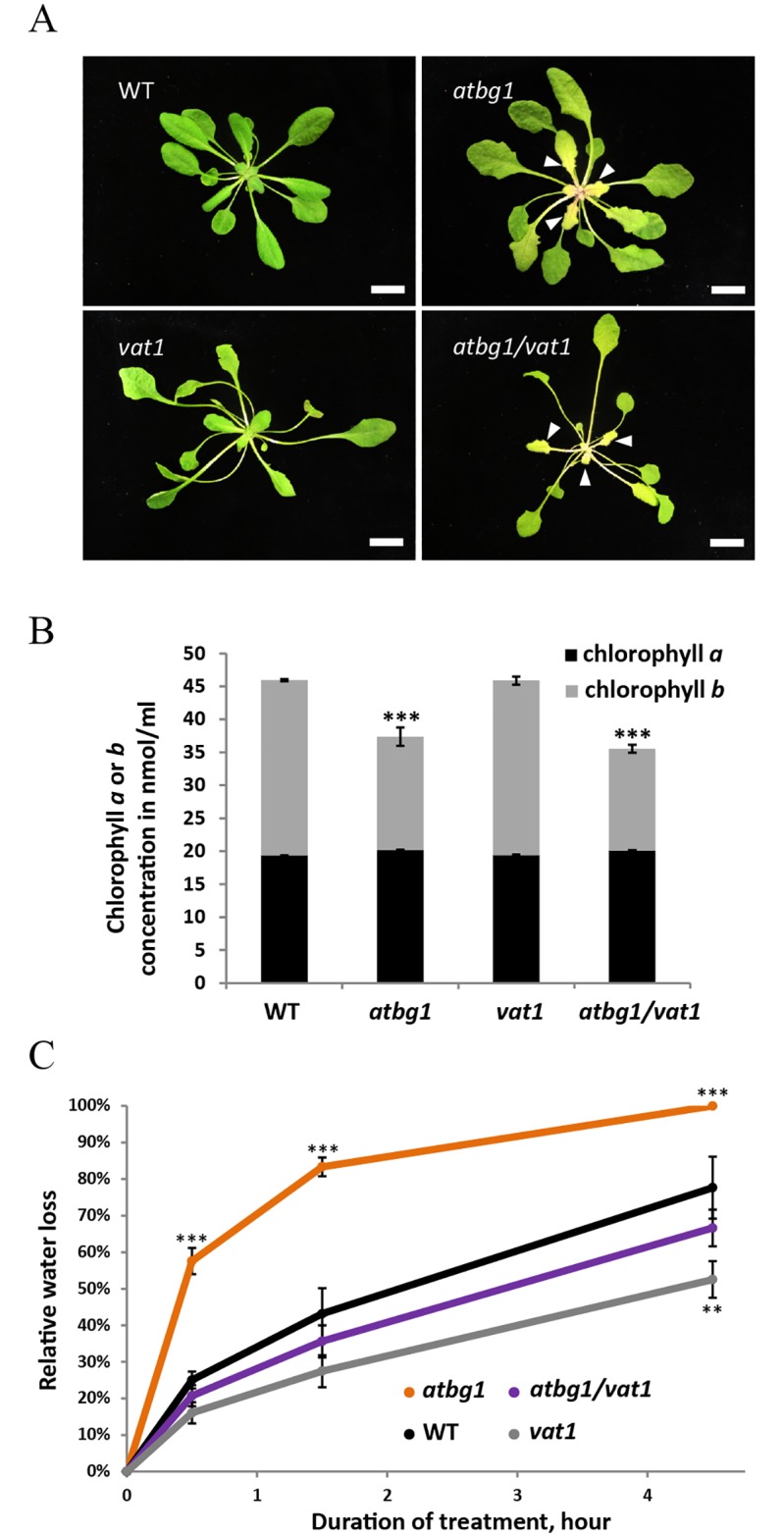
(A) Adult atbg1 plants display a yellow leaf phenotype, more pronounced in emerging leaves. vat1 petioles and hypocotyl appear longer compared to WT plants. The leaves of atbg1/vat1 double mutants show the additive effects of the developmental defects observed in each single mutant. Arrows indicate pale green to yellow leaves in atbg1 and atbg1/vat1 mutants. Bar = 1cm. (B) Chlorophyll a and b contents. A decreased concentration in chlorophyll b may contribute to the pale green to yellow color of the aerial organs in atbg1 mutants and atbg1/vat1 double mutants. Error bars are SEM (n = 3).*** P <0.001 (t-test). (C) Leaf transpiration assay. Comparison of water loss rates shows greater water loss in atbg1 mutants and restored water loss in atbg1/vat1 double mutant as compared to WT. Error bars are SEM (n = 3).***, P<0.001 (t-test); **, P<0.05 (t-test).
